A single-fibre computer enables textile networks and distributed inference
单纤维计算机实现纺织网络和分布式推理
摘要
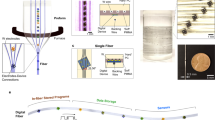
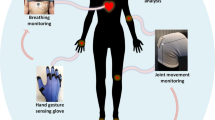
尽管可穿戴技术取得了进步1,2, 在实现持续位于人体上的分布式计算方面仍然存在障碍。本文展示了一种纺织纤维计算机,它以小于 5 克的质量,单片集成了模拟传感、数字存储、处理和通信功能。借助可折叠的中间层,微设备的二维焊盘架构被映射到符合纤维几何形状的三维圆柱布局。通过与螺旋铜微线的连接,八个微设备被热拉制成具有超过 60% 弹性的可机洗纤维。这种可编程纤维,包含一个 32 位浮点微控制器,即使在编织、梭织、针织或缝纫到服装中时,也能独立执行边缘计算任务。组装过程的通用性允许通过简单的修改来集成其他功能,包括一个可充电的纤维电源,可以为计算机供电近 6 小时。最后,我们通过实现两种无线通信方案,克服了刚性互连的长期限制,这两种方案包括编织光链路和缝纫插入的射频通信。为了证明它的实用性,我们展示了配备四个纤维计算机(每个肢体一个)的服装,这些纤维计算机运行独立训练的神经网络,在对身体活动进行分类时平均达到 67% 的准确率。然而,当联网时,使用简单的加权投票,推理准确率提高到 95%。
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access through your institution Change institution Buy or subscribe Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Fig. 1: Fabrication and mechanical characterization of a fibre computer.
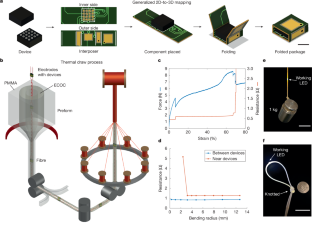 Fig. 2: Single-fibre computer electrical characterization.
Fig. 2: Single-fibre computer electrical characterization.
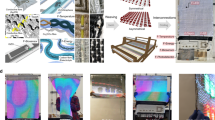
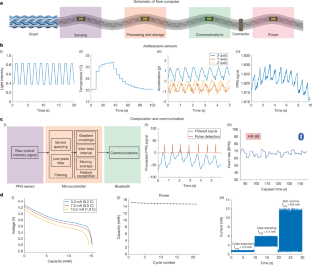 Fig. 3: Multi-fibre computer communication and fabric networks.
Fig. 3: Multi-fibre computer communication and fabric networks.
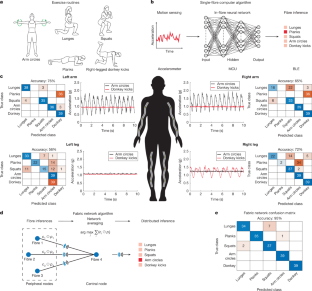
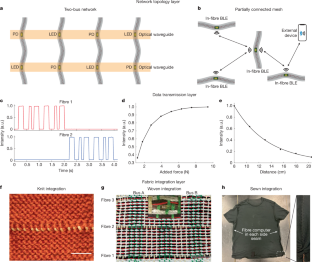 Fig. 4: Fibre computer fabric network application.
Fig. 4: Fibre computer fabric network application.
Similar content being viewed by others
Digital electronics in fibres enable fabric-based machine-learning inference
Article Open access 03 June 2021
Smart textile lighting/display system with multifunctional fibre devices for large scale smart home and IoT applications
Article Open access 10 February 2022
Electrospun bundled carbon nanofibers for skin-inspired tactile sensing, proprioception and gesture tracking applications
Article Open access 14 October 2021
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of this study are available at Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13874664)[52](https://www.nature.com/articles/</articles/s41586-024-08568-6#ref-CR52> "Gupta, N., Cheung, H. & Payra, S. Fibre Computer Repository. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13874664
\(2025\)."). [Source data](https://www.nature.com/articles/</articles/s41586-024-08568-6#Sec43>) are provided with this paper.
Code availability
Code supporting the findings of this study is publicly available at Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13874664)[52](https://www.nature.com/articles/</articles/s41586-024-08568-6#ref-CR52> "Gupta, N., Cheung, H. & Payra, S. Fibre Computer Repository. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13874664
\(2025\)."), except for code that, pursuant to copyright by Analog Devices, Inc. and Dialog Semiconductor Plc (‘vendors’), is not licenced for sharing. However, in most cases, such code is available for direct download from the vendors and has been annotated accordingly in our repository. Full code repositories are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request and with permission of the vendors, as applicable.
References
- Dunn, J., Runge, R. & Snyder, M. Wearables and the medical revolution. Per Med. 15 , 429–448 (2018). Article CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Yetisen, A. K., Martinez‐Hurtado, J. L., Ünal, B., Khademhosseini, A. & Butt, H. Wearables in medicine. Adv. Mater. 30 , e1706910 (2018). Article PubMed Google Scholar
- Martin, T., Jovanov, E. & Raskovic, D. Issues in wearable computing for medical monitoring applications: a case study of a wearable ECG monitoring device. In Digest of Papers. Fourth International Symposium on Wearable Computers 43–49 (IEEE Computer Society, 2000).
- Kim, D.-H. et al. Epidermal electronics. Science 333 , 838–843 (2011). Article ADS CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Liu, Y., Pharr, M. & Salvatore, G. A. Lab-on-skin: a review of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable health monitoring. ACS Nano 11 , 9614–9635 (2017). Article CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Yang, G.-Z., Andreu-Perez, J., Hu, X. & Thiemjarus, S. in Body Sensor Networks (ed. Yang, G.-Z.) 301–354 (Springer, 2014).
- Muzammal, M., Talat, R., Sodhro, A. H. & Pirbhulal, S. A multi-sensor data fusion enabled ensemble approach for medical data from body sensor networks. Inf. Fusion 53 , 155–164 (2020). Article Google Scholar
- Gravina, R., Alinia, P., Ghasemzadeh, H. & Fortino, G. Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: state-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 35 , 68–80 (2017). Article Google Scholar
- Tamura, T., Maeda, Y., Sekine, M. & Yoshida, M. Wearable photoplethysmographic sensors—past and present. Electronics (Basel) 3 , 282–302 (2014). MATH Google Scholar
- Mathie, M. J., Coster, A. C. F., Lovell, N. H. & Celler, B. G. Accelerometry: providing an integrated, practical method for long-term, ambulatory monitoring of human movement. Physiol. Meas. 25 , R1–R20 (2004). Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
- Wicaksono, I. et al. A tailored, electronic textile conformable suit for large-scale spatiotemporal physiological sensing in vivo. npj Flexible Electron. 4 , 5 (2020). Article Google Scholar
- Shi, J. et al. Smart textile‐integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications. Adv. Mater. 32 , e1901958 (2020). Article PubMed Google Scholar
- Chen, G. et al. Electronic textiles for wearable point-of-care systems. Chem. Rev. 122 , 3259–3291 (2022). Article CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Yan, W. et al. Advanced multimaterial electronic and optoelectronic fibers and textiles. Adv. Mater. 31 , e1802348 (2019). Article PubMed Google Scholar
- Yan, W. et al. Thermally drawn advanced functional fibers: new frontier of flexible electronics. Mater. Today 35 , 168–194 (2020). Article CAS MATH Google Scholar
- Bayindir, M., Abouraddy, A. F., Arnold, J., Joannopoulos, J. D. & Fink, Y. Thermal‐sensing fiber devices by multimaterial codrawing. Adv. Mater. 18 , 845–849 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar
- Zhang, T. et al. High-performance, flexible, and ultralong crystalline thermoelectric fibers. Nano Energy 41 , 35–42 (2017). Article MATH Google Scholar
- Yan, W. et al. Single fibre enables acoustic fabrics via nanometre-scale vibrations. Nature 603 , 616–623 (2022). Article ADS CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Gumennik, A. et al. All‐in‐fiber chemical sensing. Adv. Mater. 24 , 6005–6009 (2012). Article CAS PubMed MATH Google Scholar
- Pan, Z. et al. All-in-one stretchable coaxial-fiber strain sens