在 SGLang 中实现 Flash Attention 后端:基础与 KV Cache
在 SGLang 中实现 Flash Attention 后端 - 基础与 KV Cache
2025年4月26日 作者:
Biao He
Qingquan Song
0x0. 简介
在过去的几周里,我们已经在 SGLang 中端到端地实现了 Flash Attention Backend,它现在是 SGLang 0.4.6版本的默认 attention 后端。
 在这个过程中,我们学到了很多关于 Attention Backend 在现代 LLM 服务引擎中如何运作的知识,并且对 Flash Attention 本身有了更深入的理解。
在这个过程中,我们学到了很多关于 Attention Backend 在现代 LLM 服务引擎中如何运作的知识,并且对 Flash Attention 本身有了更深入的理解。
在本系列文章中,我们将逐步介绍实现细节,分享我们希望能够帮助任何希望在 LLM 服务引擎中实现自己的 attention 后端的人的见解。
本系列文章的目录
本系列文章将分为三个部分:
- 第一部分: 基础、KV Cache 和 CUDA Graph 支持(本文)
- 第二部分: 推测性解码支持(即将推出)
- 第三部分: MLA、Llama 4、滑动窗口和多模态支持(即将推出)
SGLang 中 Attention Backend 的最新状态
后端 | Page Size > 1 | Spec Decoding | MLA | Llama 4 | MultiModal | FP8
---|---|---|---|---|---|---
FlashAttention | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅
FlashInfer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌
Triton | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅
Torch | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
基准测试结果
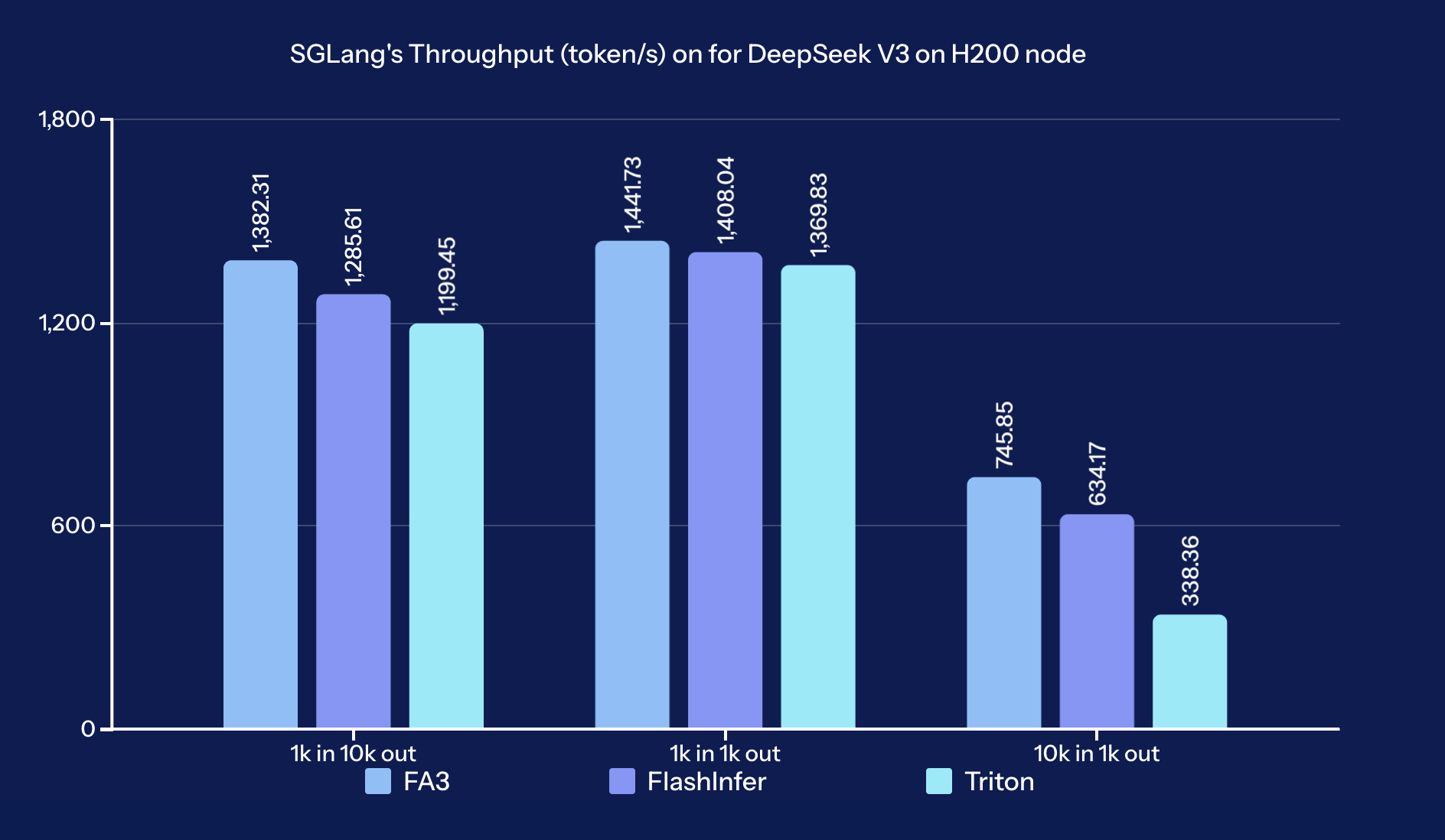 基准测试结果表明,FA3 在所有测试场景中始终提供最高的吞吐量,优于 FlashInfer 和 Triton,尤其是在输入或输出大小增加时。
基准测试结果表明,FA3 在所有测试场景中始终提供最高的吞吐量,优于 FlashInfer 和 Triton,尤其是在输入或输出大小增加时。
0x1. 背景和动机
什么是 Flash Attention?
Flash Attention1 是一种 IO 感知的精确 attention 算法,它使用 tiling 来减少 GPU 高带宽内存 (HBM) 和 GPU 片上 SRAM 之间的内存读取/写入次数。
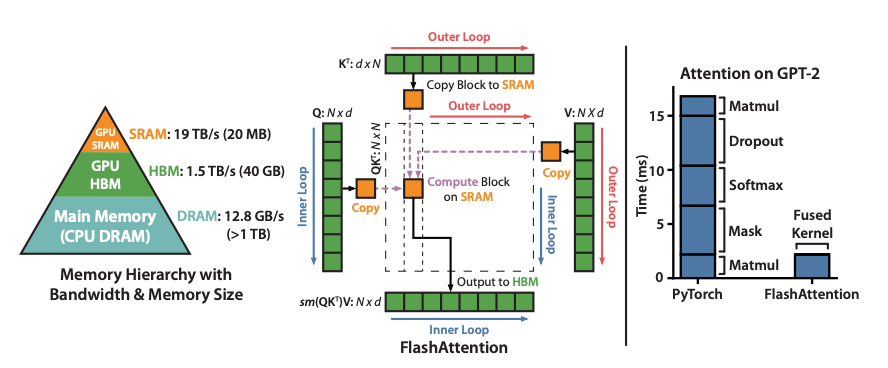 它已被广泛用于 LLM 推理和训练,并且是现代服务引擎(如 SGLang、vLLM 等)中的默认 attention 后端。
它已被广泛用于 LLM 推理和训练,并且是现代服务引擎(如 SGLang、vLLM 等)中的默认 attention 后端。
在大多数情况下,可以将其视为黑盒。 但是,通过了解其核心逻辑,我们可以更智能地使用它。
我强烈推荐这篇文章2来理解 Flash Attention 的核心逻辑。 我也有一篇关于 什么是 Flash Attention? 的博文,其中我从代码层面做了简要介绍。
Attention Backend 在 SGLang 中如何工作
SGLang 架构
SGLang 作为一个现代的 LLM 服务引擎,有三个主要组件(在逻辑视图中)3:
- Server Components: 负责处理传入的请求并发送响应。
- Scheduler Components: 负责构建 batches 并发送给 Worker。
- Model Components: 负责模型推理。
让我们重点关注上图中的模型前向传播。
在步骤 8 中: ModelRunner 处理 ForwardBatch 并调用 model.forward 来执行模型的前向传播。
在步骤 9 中: model.forward 将调用每一层的 forward 函数,并且大部分时间都花在 self-attention 部分。 因此,attention 后端成为模型推理的瓶颈。 除了性能之外,还有许多不同类型的 attention 变体,例如 MHA、MLA、GQA、滑动窗口、局部 Attention,它们需要经过精心优化的 attention 后端实现。
Attention Backend 继承关系
这是 attention 变体的继承关系: 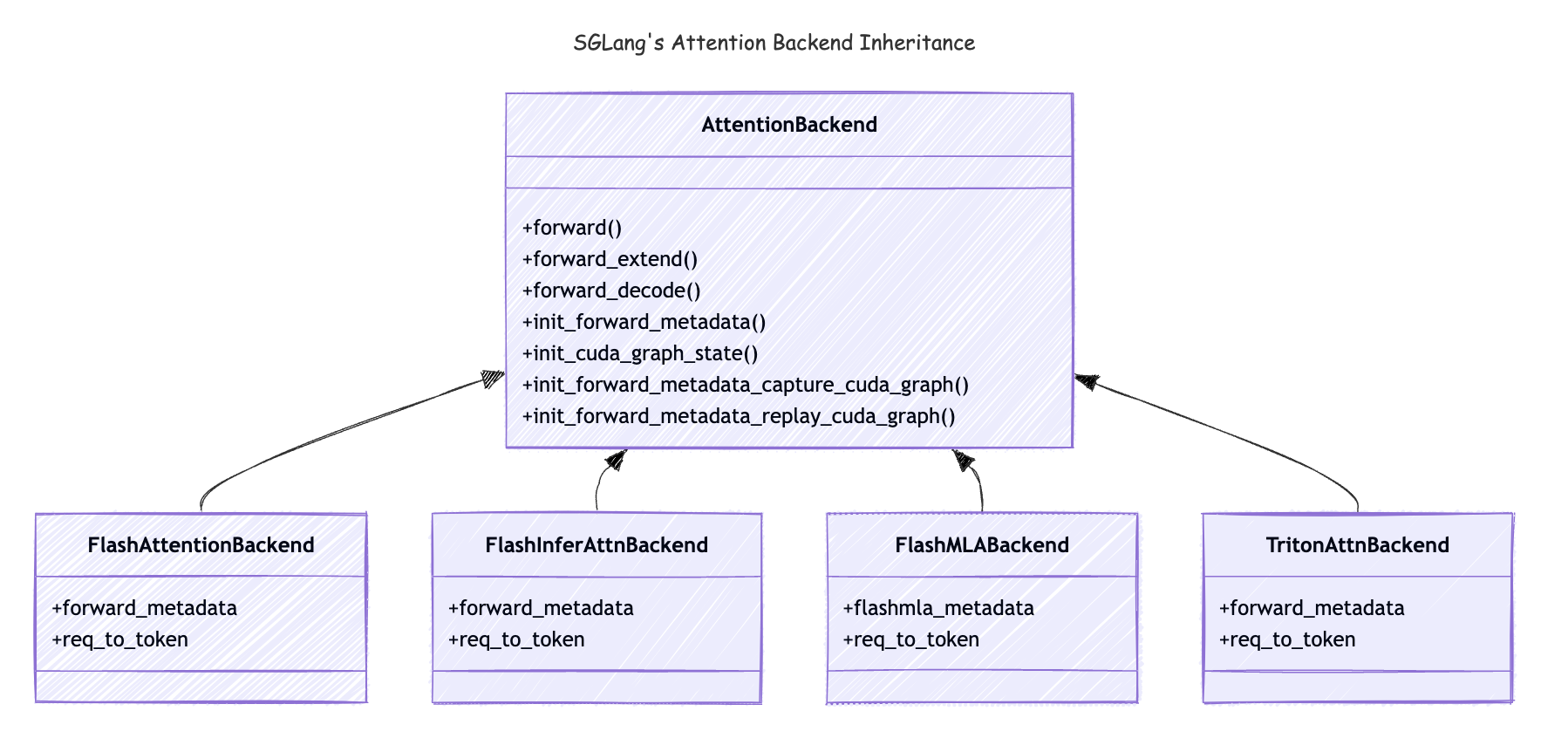
让我们浏览 AttentionBackend 类中的方法,看看 SGLang 中 attention 后端的骨架是什么。
forward(): 当model.forward()被调用时,AttentionBackend中的forward方法将被调用。 它将根据forward_batch.forward_mode调用forward_extend()和forward_decode。 在这篇博客中,我们只关注EXTEND和DECODE模式。forward_extend(): 当forward_mode为EXTEND时,将为每个 layer 调用此方法。forward_decode(): 当forward_mode为DECODE时,将为每个 layer 调用此方法。init_cuda_graph_state(): 此方法将在服务器启动期间被调用,它将预先分配那些将在 CUDA Graph 重放中使用的 tensors。init_forward_metadata(): 此方法将在调用model.forward()时被调用。 它可以为整个model.forward()调用预先计算一些元数据,并由每个 layer 重用,这对于加速模型推理至关重要。 具有讽刺意味的是,此元数据是 attention 后端中最复杂的部分,一旦我们设置好它,在此上下文中调用 softmax(QK⊤)V 计算就非常简单了。init_forward_metadata_capture_cuda_graph: 此方法将在服务器启动期间被调用,CUDAGraphRunner将在 CUDA Graph 捕获期间调用此方法。 CUDA Graph 将存储在CUDAGraphRunner的self.graphs对象中的内存中。init_forward_metadata_replay_cuda_graph: 此方法将在调用每个 layer 的forward_decode时被调用。 它将为forwade_decode调用设置元数据,以确保可以正确完成 CUDA Graph 重放。
到目前为止,我们已经涵盖了我们需要为 attention 后端实现的所有方法。 我们将在以下部分中讨论它。
KV Cache 在 SGLang 中如何工作
您可能对每个 Attention Backend 类中为什么都有一个 req_to_token 感到好奇。 我并不是偶然把它放在那里的。 实际上,KV Cache 作为所有 LLM 服务引擎的骨干,对于 Attention Backend 来说也非常关键,所以让我们简单地看一下它。
有两种级别的内存池来管理 KV cache4。 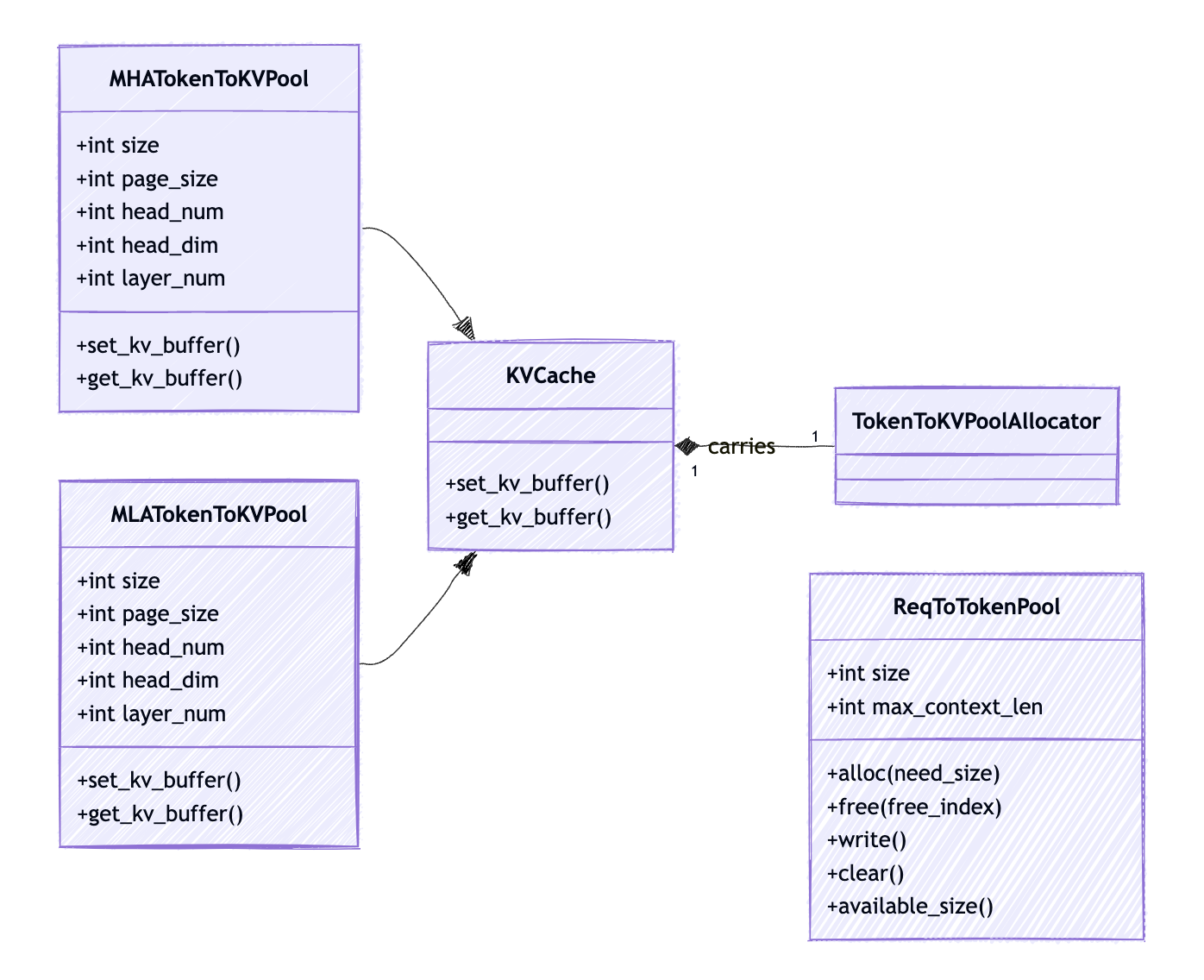
req_to_token_pool
从请求到其 tokens 的 KV cache indices 的映射。 这就是我们在 Attention Backend 图中提到的 req_to_token。
- Shape: 最大允许请求数(由参数
max-running-requests设置为并发运行的最大请求数)* 每个请求的最大上下文长度(由配置model_config.context_len设置) - Access:
- Dim0:
req_pool_indices识别特定的请求 - Dim1:请求中的 token 位置(从 0、1、2...开始),识别请求中的特定 token
- Value:token 的
out_cache_loc,它指向与 Dim0 和 Dim1 标识的 token 关联的 KV cache indices
- Dim0:
token_to_kv_pool
req_to_token_pool 维护请求与 tokens KV cache indices 之间的映射,token_to_kv_pool 进一步将 token 从其 KV cache indices 映射到其真实的 KV cache 数据。 请注意,对于不同的 attention 实现,例如 MHA、MLA、Double Sparsity,token_to_kv_pool 可以有不同的实现。
- Layout: Layers 数量 * 最大允许 Tokens 数量 * Head 数量 * Head Dimension
- Access:
- Dim0:
layer_id识别特定的 layer - Dim1:
out_cache_loc识别特定的 KV cache indices(空闲槽) - Dim2:Head
- Dim3:Head Dimension
- Value:k_buffer 的
cache_k和 v_buffer 的cache_v,真实的 KV Cache 数据
- Dim0:
请注意,我们通常一起检索整个 layer 的 KV Cache,因为我们需要请求中所有先前 tokens 的 KV 来进行前向传播。
在 attention 后端中,我们只需要知道 req_to_token_pool 是什么,其余的 KV Cache 管理对于 attention 后端是透明的。
让我们给出一个关于 req_to_token_pool 样子的直观示例:
- 假设我们有 2 个请求,每个请求有 7 个 tokens。
- 那么
req_to_token_pool是一个 shape 为 (2, 7) 的 tensor,其中每个条目将请求中的一个 token 映射到其相应的 KV cache 索引。
req_to_token_pool = [
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
]
seq_lens 是 [7, 7]。
3. 在一个 forward_extend 将一个新 token 添加到每个请求之后,req_to_token_pool 将更新为:
req_to_token_pool = [
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 15],
[8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16]
]
seq_lens 是 [8, 8]。
4. 如果第一个请求完成,我们为第二个请求运行另一个 decode,req_to_token_pool 将更新为:
req_to_token_pool = [
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 15],
[8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17]
]
seq_lens 是 [8, 9]。
通过以上关于 KV Cache 结构的知识,我们现在有了实现 FlashAttention 后端的基础。 下一步是为 flash_attn_with_kvcache API 识别正确的参数,以创建一个最小的工作实现。
有关 KV Cache 的更多详细信息,请参阅 Awesome-ML-SYS-Tutorial: KV Cache Code Walkthrough。
0x2. FlashAttention3 后端基本实现
好的,让我们开始深入研究 SGLang 中 FlashAttention 后端的实现。
这是基本实现的 PR:sgl-project/sglang#4680。 为了简洁起见,我简化了这篇博客中的代码,只关注核心逻辑。
Tri Dao 的 FlashAttention 3 Kernel API
Tri Dao 为 Flash Attention 3 提供了几个公共 API,入口点是 hopper/flash_attn_interface.py。
我们选择 flash_attn_with_kvcache 的主要原因有两个:它消除了手动组装 key-value 对的开销(通过直接接受整个页表),并且它为 Paged KV Cache(Page Size > 1)提供原生支持,这在 flash_attn_varlen_func 中不可用。
让我们快速浏览一下 flash_attn_with_kvcache API:
# 为了简洁起见,我们省略了一些参数
def flash_attn_with_kvcache(
q,
k_cache,
v_cache,
cache_seqlens: Optional[Union[(int, torch.Tensor)]] = None,
page_table: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
cu_seqlens_q: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
cu_seqlens_k_new: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
max_seqlen_q: Optional[int] = None,
causal=False,
):
"""
Arguments:
q: (batch_size, seqlen, nheads, headdim)
k_cache: (batch_size_cache, seqlen_cache, nheads_k, headdim) if there's no page_table,
or (num_blocks, page_block_size, nheads_k, headdim) if there's a page_table (i.e. paged KV cache)
page_block_size must be a multiple of 256.
v_cache: (batch_size_cache, seqlen_cache, nheads_k, headdim_v) if there's no page_table,
or (num_blocks, page_block_size, nheads_k, headdim_v) if there's a page_table (i.e. paged KV cache)
cache_seqlens: int, or (batch_size,), dtype torch.int32. The sequence lengths of the
KV cache.
page_table [optional]: (batch_size, max_num_blocks_per_seq), dtype torch.int32.
The page table for the KV cache. It will derived attention backend's req_to_token_pool.
cu_seqlens_q: (batch_size,), dtype torch.int32. The cumulative sequence lengths of the query.
cu_seqlens_k_new: (batch_size,), dtype torch.int32. The cumulative sequence lengths of the new key/value.
max_seqlen_q: int. The maximum sequence length of the query.
causal: bool. Whether to apply causal attention mask (e.g., for auto-regressive modeling).
Return:
out: (batch_size, seqlen, nheads, headdim).
"""
初始化
通过以上信息,现在的任务非常明确,我们只需要找出 flash_attn_with_kvcache API 的那些参数,我们就可以实现 FlashAttention 后端的最低限度。
让我们从 FlashAttentionBackend 类和 FlashAttentionMetadata 类的初始化开始。
@dataclass
class FlashAttentionMetadata:
"""Metadata which will be created once during model forward and reused across layers forward."""
cache_seqlens_int32: torch.Tensor = None # Sequence Lengths in int32
max_seq_len_q: int = 0 # Max Sequence Length for Query
max_seq_len_k: int = 0 # Max Sequence Length for Key
cu_seqlens_q: torch.Tensor = None # Cumulative Sequence Lengths for Query
cu_seqlens_k: torch.Tensor = None # Cumulative Sequence Lengths for Key
page_table: torch.Tensor = None # Page Table indicate the KV Indices for each sequence
class FlashAttentionBackend(AttentionBackend):
"""FlashAttention backend implementation."""
def __init__(
self,
model_runner: ModelRunner,
):
super().__init__()
self.forward_metadata: FlashAttentionMetadata = None # metadata for the forward pass
self.max_context_len = model_runner.model_config.context_len # max context length set by model config
self.device = model_runner.device # device of the model (GPU)
self.decode_cuda_graph_metadata = {} # metadata for accelerating decode process
self.req_to_token = model_runner.req_to_token_pool.req_to_token # map from a request to its tokens' KV cache indices
初始化 Forward Metadata
def init_forward_metadata(self, forward_batch: ForwardBatch):
"""Initialize forward metadata during model forward and reused across layers forward
Args:
forward_batch: `ForwardBatch` object, contains the forward batch information like forward_mode, batch_size, req_pool_indices, seq_lens, out_cache_loc
"""
# Initialize metadata
metadata = FlashAttentionMetadata()
# Get batch size
batch_size = forward_batch.batch_size
# Get original sequence lengths in batch
seqlens_in_batch = forward_batch.seq_lens
# Get device of the model, e.g: cuda
device = seqlens_in_batch.device
# Get sequence lengths in int32
metadata.cache_seqlens_int32 = seqlens_in_batch.to(torch.int32)
# Get max sequence length for key
# Note that we use seq_lens_cpu to skip a device sync
# See PR: https://github.com/sgl-project/sglang/pull/4745
metadata.max_seq_len_k = forward_batch.seq_lens_cpu.max().item()
# Get cumulative sequence lengths for key
metadata.cu_seqlens_k = torch.nn.functional.pad(
torch.cumsum(seqlens_in_batch, dim=0, dtype=torch.int32), (1, 0)
)
# Get page table, we cutoff by the max sequence length
metadata.page_table = forward_batch.req_to_token_pool.req_to_token[
forward_batch.req_pool_indices, : metadata.max_seq_len_k
]
if forward_batch.forward_mode == ForwardMode.EXTEND:
# Get sequence lengths in int32
metadata.max_seq_len_q = max(forward_batch.extend_seq_lens_cpu)
metadata.cu_seqlens_q = torch.nn.functional.pad(
torch.cumsum(forward_batch.extend_seq_lens, dim=0, dtype=torch.int32), (1, 0)
)
elif forward_batch.forward_mode == ForwardMode.DECODE:
# For decoding, query length is always 1
metadata.max_seq_len_q = 1
# Get cumulative sequence lengths for query
metadata.cu_seqlens_q = torch.arange(
0, batch_size + 1, dtype=torch.int32, device=device
)
# Save metadata, hence forward_extend and forward_decode could reuse it
self.forward_metadata = metadata
Forward Extend 和 Forward Decode
在模型前向传播中,model_runner 将调用 init_forward_metadata 来初始化 attention 后端的元数据,然后调用实际的 forward_extend 和 forward_decode。 因此,forward_extend 和 forward_decode 的实现非常简单。
def forward_extend(
self,
q: torch.Tensor,
k: torch.Tensor,
v: torch.Tensor,
layer: RadixAttention,
forward_batch: ForwardBatch,
save_kv_cache=True,
):
# Get the KV Cache location from the forward batch
cache_loc = forward_batch.out_cache_loc
# Save the KV Cache for the new tokens
if save_kv_cache:
forward_batch.token_to_kv_pool.set_kv_buffer(layer, cache_loc, k, v)
# Use precomputed metadata
metadata = self.forward_metadata
# Get the KV Cache for the previous tokens
key_cache, value_cache = forward_batch.token_to_kv_pool.get_kv_buffer(layer.layer_id)
o = flash_attn_with_kvcache(
q=q.contiguous().view(-1, layer.tp_q_head_num, layer.head_dim),
k_cache=key_cache.unsqueeze(1),
v_cache=value_cache.unsqueeze(1),
page_table=metadata.page_table,
cache_seqlens=metadata.cache_seqlens_int32,
cu_seqlens_q=metadata.cu_seqlens_q,
cu_seqlens_k_new=metadata.cu_seqlens_k,
max_seqlen_q=metadata.max_seq_len_q,
causal=True, # for auto-regressive attention
)
# forward_decode 与 forward_extend 相同,我们已经在 init_forward_metadata 中以不同的方式设置了元数据
到目前为止,已经实现了一个最低限度的 FlashAttention 后端。 我们可以使用此后端来执行 attention 前向传播。
0x3. CUDA Graph 支持
什么是 CUDA Graph?
CUDA Graph 是 NVIDIA 的 CUDA 平台中的一项功能,允许您捕获一系列 GPU 操作,并将其作为单个优化单元进行重放。 传统上,来自 CPU 的每个 GPU kernel 启动都会产生一些启动延迟,并且 CPU 必须按顺序协调每个步骤。 这种开销可能会变得很大,尤其是对于具有许多小 kernels 的工作负载。5
使用 CUDA Graph,您可以将一系列操作(例如图中的 A、B、C、D、E)记录到一个图中,然后一次性启动整个图。 这种方法消除了重复的 CPU 启动开销,并使 GPU 能够更有效地执行操作,从而显着节省时间。 下图说明了这个概念:顶部显示了传统方法,其中每个 kernel 启动都会产生 CPU 开销。 底部显示了 CUDA Graph 方法,其中整个序列作为单个图启动,从而减少了 CPU 时间并提高了整体吞吐量。
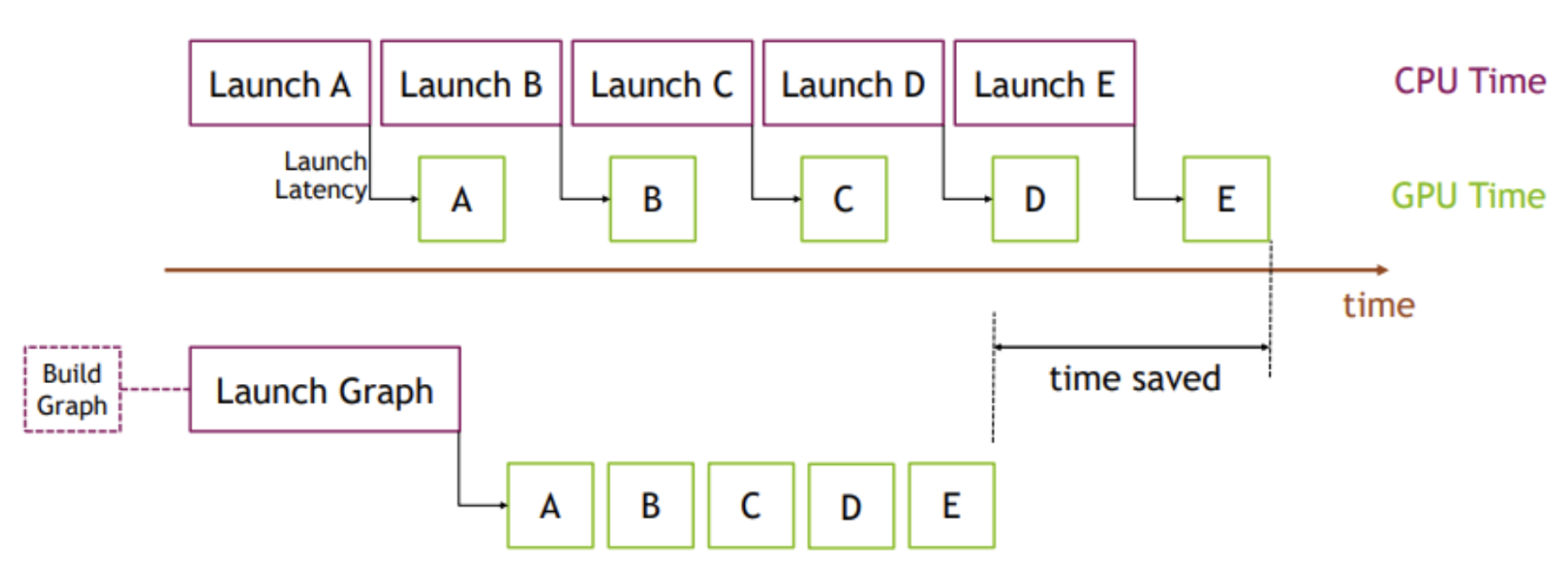 实际上,我发现现代 LLM 服务引擎中的许多显着加速来自于并行化多个工作负载并重叠其执行。 我可以轻松地举几个例子:
实际上,我发现现代 LLM 服务引擎中的许多显着加速来自于并行化多个工作负载并重叠其执行。 我可以轻松地举几个例子:
我相信这种简单但有效的理念还有更多的机会,它让我非常兴奋地看到越来越多的酷项目建立在下一代硬件之上。
CUDA Graph 在 SGLang 中如何工作
在 SGLang 中,CUDA Graph 的捕获和重放由 CUDAGraphRunner 类完成。 鉴于该框架已经对 CUDAGraphRunner 如何与 attention 后端协同工作有一个相当不错的设计,我们可以专注于实现以下三种方法:
init_cuda_graph_state()init_forward_metadata_capture_cuda_graph()init_forward_metadata_replay_cuda_graph()
您可以在下图中找到 CUDAGraphRunner 如何与 attention 后端协同工作的详细流程:
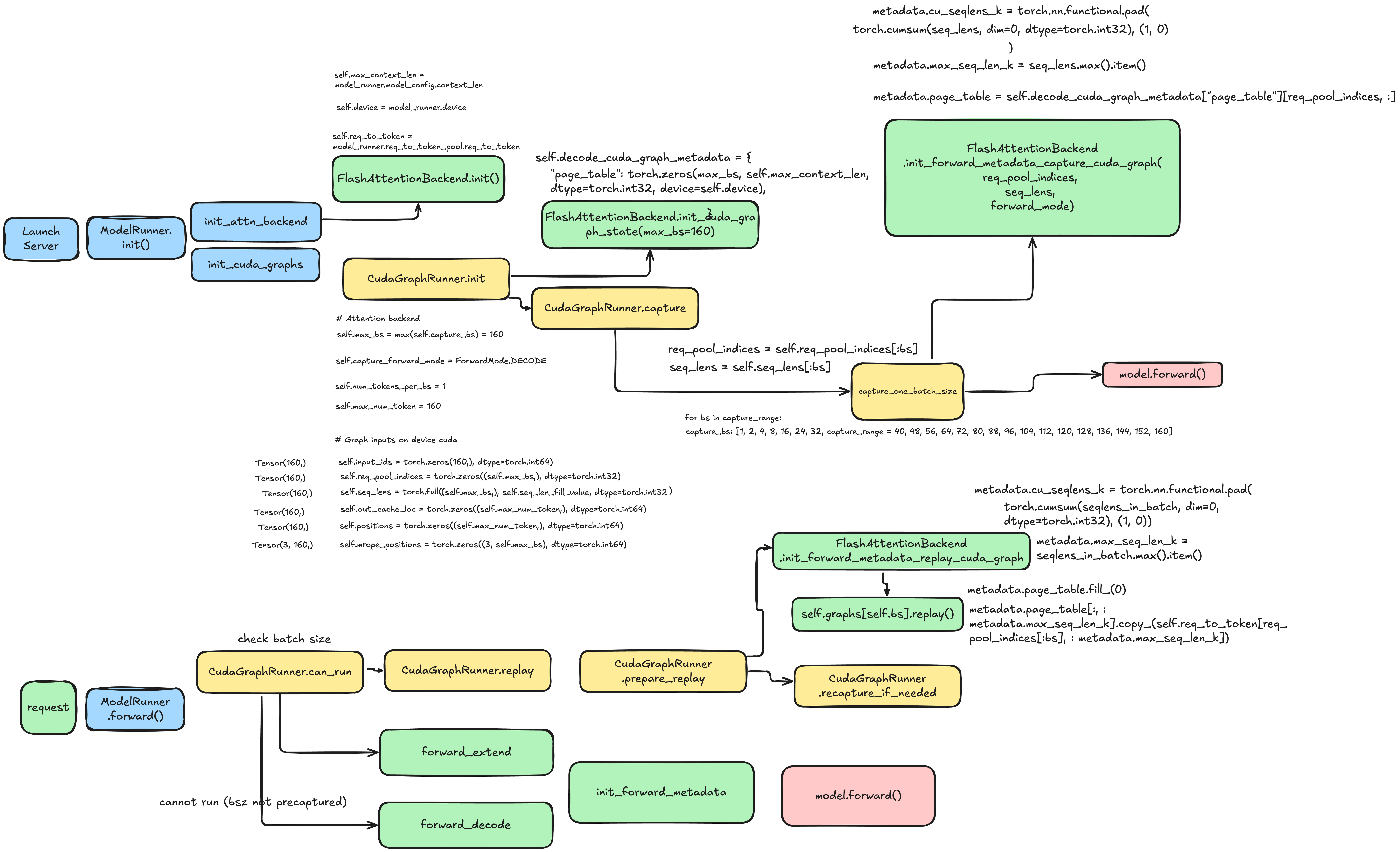
初始化 CUDA Graph 状态
def init_cuda_graph_state(self, max_bs: int):
"""Initialize CUDA graph state for the attention backend.
Args:
max_bs (int): Maximum batch size to support in CUDA graphs
This creates fixed-size tensors during server startup that will be reused during CUDA graph replay to avoid memory allocations.
"""
self.decode_cuda_graph_metadata = {
# Sequence Lengths in int32 (batch_size)
"cache_seqlens": torch.zeros(max_bs, dtype=torch.int32, device=self.device),
# Cumulative Sequence Lengths for Query (batch_size + 1)
"cu_seqlens_q": torch.arange(
0, max_bs + 1, dtype=torch.int32, device=self.device
),
# Cumulative Sequence Lengths for Key (batch_size + 1)
"cu_seqlens_k": torch.zeros(
max_bs + 1, dtype=torch.int32, device=self.device
),
# Page Table for token mapping from request to tokens' KV cache indices (batch_size, max_context_len)
"page_table": torch.zeros(
max_bs,
self.max_context_len,
dtype=torch.int32,
device=self.device,
),
}
值得注意的是,我们发现对于 tensor 类型的元数据,我们需要先初始化,然后将值复制到预分配的 tensors 中,否则 CUDA Graph 将无法工作。 对于标量类型的那些元数据(例如:
max_seq_len_q、max_seq_len_k),我们可以直接创建新变量。
为捕获准备元数据
def init_forward_metadata_capture_cuda_graph(
self,
bs: int,
num_tokens: int,
req_pool_indices: torch.Tensor,
seq_lens: torch.Tensor,
encoder_lens: Optional[torch.Tensor],
forward_mode: ForwardMode,
):
"""Initialize forward metadata for capturing CUDA graph."""
metadata = FlashAttentionMetadata()
device = seq_lens.device
batch_size = len(seq_lens)
metadata.cache_seqlens_int32 = seq_lens.to(torch.int32)
if forward_mode == ForwardMode.DECODE:
metadata.cu_seqlens_q = torch.arange(
0, batch_size + 1, dtype=torch.int32, device=device
)
metadata.max_seq_len_k = seq_lens.max().item()
metadata.cu_seqlens_k = torch.nn.functional.pad(
torch.cumsum(seq_lens, dim=0, dtype=torch.int32), (1, 0)
)
metadata.page_table = self.decode_cuda_graph_metadata["page_table"][
req_pool_indices, :
]
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Forward mode {forward_mode} is not supported yet")
self.decode_cuda_graph_metadata[bs] = metadata
说实话,我们不太关心在
init_forward_metadata_capture_cuda_graph中设置的实际值,因为我们会在init_forward_metadata_replay_cuda_graph中覆盖它。 我们只需要确保 tensor shape 正确即可。
为重放准备元数据
def init_forward_metadata_replay_cuda_graph(
self,
bs: int,
req_pool_indices: torch.Tensor,
seq_lens: torch.Tensor,
seq_lens_sum: int,
encoder_lens: Optional[torch.Tensor],
forward_mode: ForwardMode,
seq_lens_cpu: Optional[torch.Tensor],
out_cache_loc: torch.Tensor = None,
):
"""Initialize forward metadata for replaying CUDA graph."""
# Get the sequence lengths in batch, we slice it out from the preallocated tensors
seq_lens = seq_lens[:bs]
# Get the sequence lengths in CPU, we slice it out from the preallocated tensors
seq_lens_cpu = seq_lens_cpu[:bs]
# Get the request pool indices, we slice it out from the preallocated tensors
req_pool_indices = req_pool_indices[:bs]
# Get the device of the model
device = seq_lens.device
# Get the metadata for the decode, which have been precomputed in init_forward_metadata_capture_cuda_graph() and initialized in init_cuda_graph_state()
metadata = self.decode_cuda_graph_metadata[bs]
if forward_mode == ForwardMode.DECODE:
# Update the sequence lengths with actual values
metadata.cache_seqlens_int32 = seq_lens.to(torch.int32)
# Update the maximum sequence length for key with actual values
metadata.max_seq_len_k = seq_lens_cpu.max().item()
# Update the cumulative sequence lengths for key with actual values