使用 LLM 为文档构建实时知识图谱
使用 LLM 为文档构建实时知识图谱
2025年4月29日 · 阅读时长 7 分钟

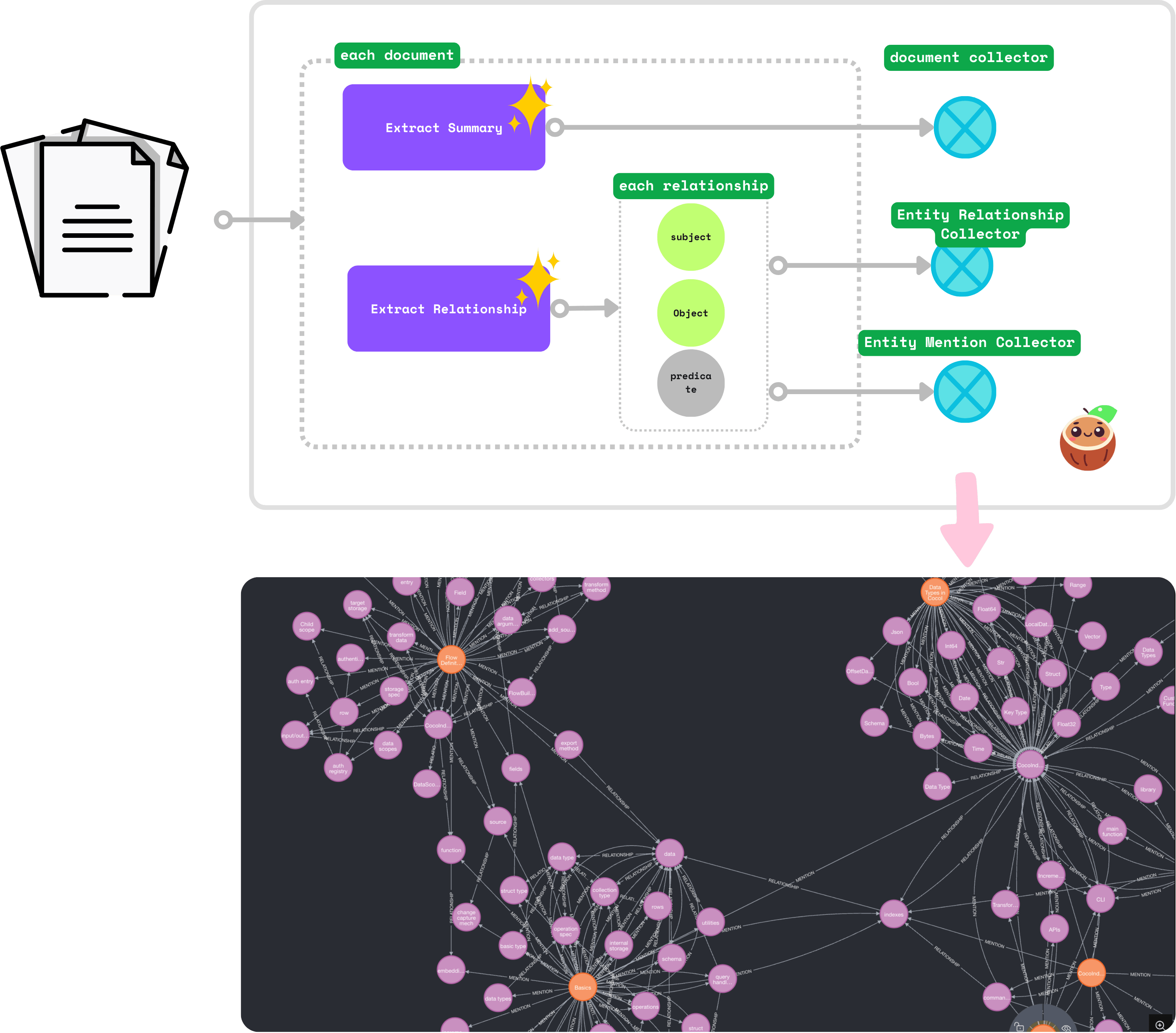 借助持续的源更新,构建和维护知识图谱变得非常容易。在本博客中,我们将处理一系列文档(以 CocoIndex 文档为例)。我们将使用 LLM 提取每个文档中概念之间的关系。我们将生成两种关系:
借助持续的源更新,构建和维护知识图谱变得非常容易。在本博客中,我们将处理一系列文档(以 CocoIndex 文档为例)。我们将使用 LLM 提取每个文档中概念之间的关系。我们将生成两种关系:
- 主体和对象之间的关系。例如,“CocoIndex 支持 Incremental Processing”
- 文档中实体的提及。例如,“core/basics.mdx”提到了
CocoIndex和Incremental Processing。
源代码可在 CocoIndex Examples - docs_to_knowledge_graph 中找到。
 我们正在不断改进,更多功能和示例即将推出。请继续关注并通过为我们的 GitHub repo 加星标来关注我们的进展。
我们正在不断改进,更多功能和示例即将推出。请继续关注并通过为我们的 GitHub repo 加星标来关注我们的进展。
前提条件
- 安装 PostgreSQL。CocoIndex 内部使用 PostgreSQL 进行增量处理。
- 安装 Neo4j,一个图数据库。
- 配置您的 OpenAI API 密钥。或者,您可以切换到 Ollama,它在本地运行 LLM 模型 - 指南。
文档
您可以在 此处 阅读有关 Property Graph Targets 的官方 CocoIndex 文档。
构建知识图谱的数据流
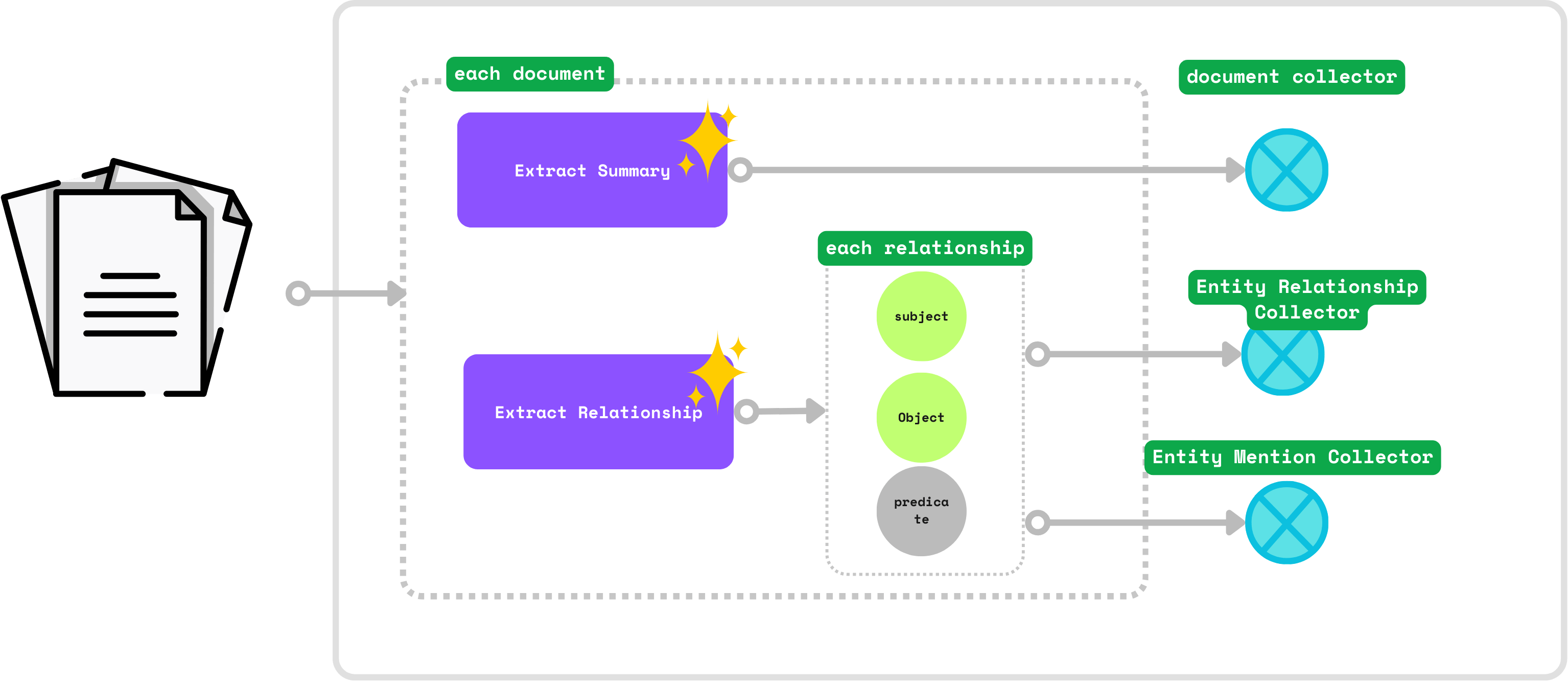
添加文档作为源
我们将处理来自 docs/core 目录的 CocoIndex 文档 markdown 文件(.md、.mdx)(markdown 文件,[已部署的文档](https://cocoindex.io/blogs/knowledge-graph-for-docs/https:/cocoindex.io/docs/core/basics))。
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="DocsToKG")defdocs_to_kg_flow(flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope): data_scope["documents"]= flow_builder.add_source( cocoindex.sources.LocalFile(path="../../docs/docs/core", included_patterns=["*.md","*.mdx"]))
这里,flow_builder.add_source 创建一个 KTable。filename 是 KTable 的键。
添加数据收集器
在根范围添加收集器:
document_node = data_scope.add_collector()entity_relationship = data_scope.add_collector()entity_mention = data_scope.add_collector()
document_node收集文档。例如,core/basics.mdx是一个文档。entity_relationship收集关系。例如,“CocoIndex 支持 Incremental Processing”表示CocoIndex和Incremental Processing之间的关系。entity_mention收集文档中实体的提及。例如,core/basics.mdx提到了CocoIndex和Incremental Processing。
处理每个文档并提取摘要
定义一个 DocumentSummary 数据类来提取文档的摘要。
@dataclasses.dataclassclassDocumentSummary: title:str summary:str
在流程中,使用 cocoindex.functions.ExtractByLlm 进行结构化输出。
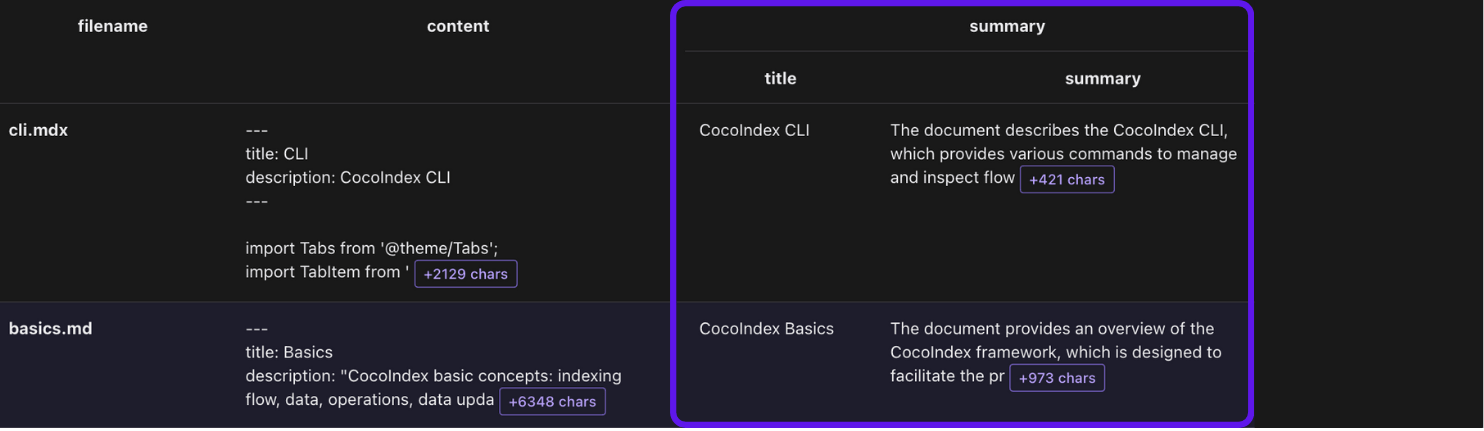
with data_scope["documents"].row()as doc: doc["summary"]= doc["content"].transform( cocoindex.functions.ExtractByLlm( llm_spec=cocoindex.LlmSpec( api_type=cocoindex.LlmApiType.OPENAI, model="gpt-4o"), output_type=DocumentSummary, instruction="Please summarize the content of the document.")) document_node.collect( filename=doc["filename"], title=doc["summary"]["title"], summary=doc["summary"]["summary"])
doc["summary"] 向 KTable data_scope["documents"] 添加一个新列。
使用 LLM 从文档中提取关系
定义一个数据类来表示 LLM 提取的关系。
@dataclasses.dataclassclassRelationship:""" Describe a relationship between two entities. Subject and object should be Core CocoIndex concepts only, should be nouns. For example, `CocoIndex`, `Incremental Processing`, `ETL`, `Data` etc. """ subject:str predicate:strobject:str
该数据类定义了知识图谱关系。我们建议在类级别的文档字符串中放置详细的说明,以帮助 LLM 正确提取关系。
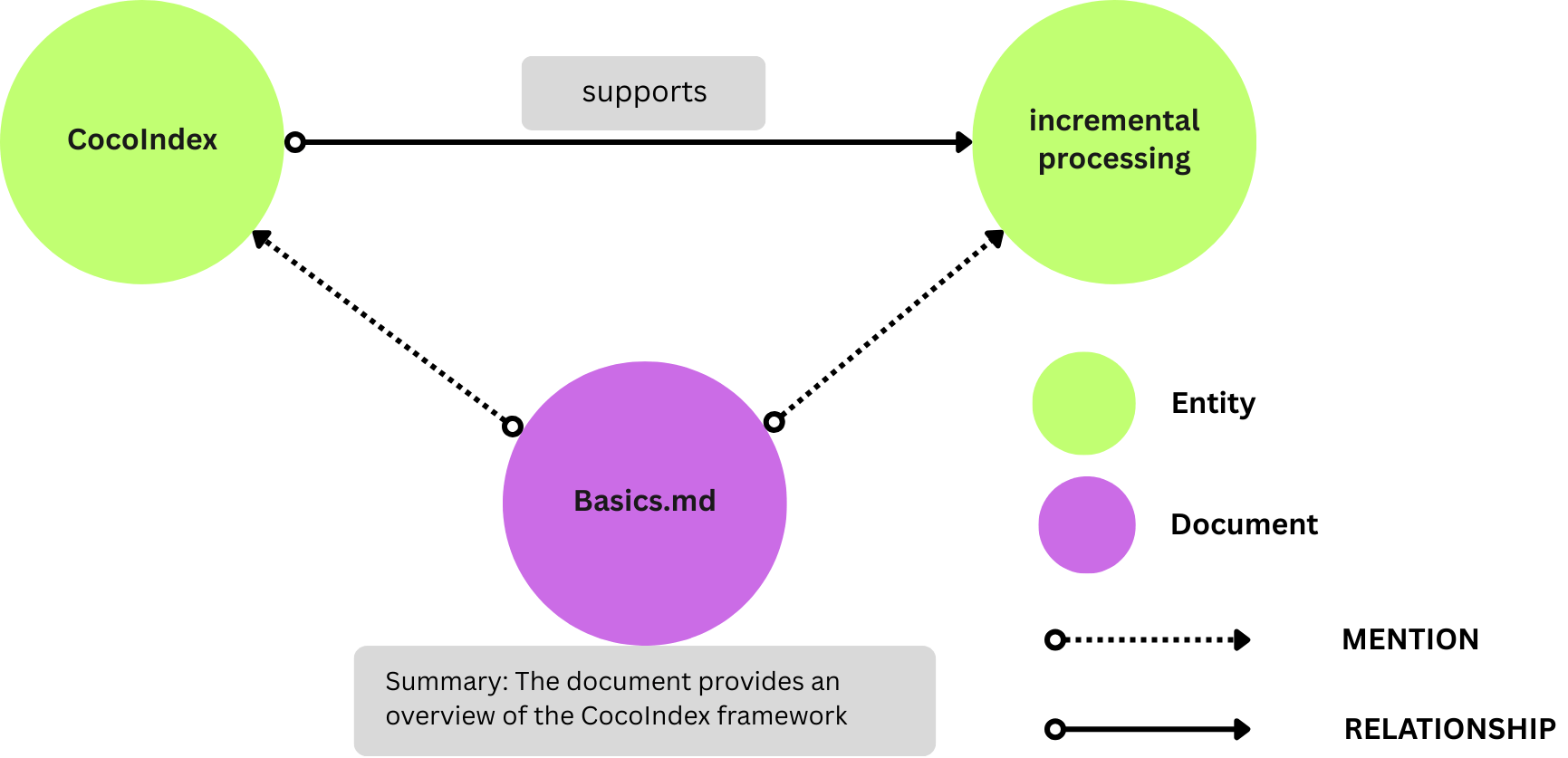
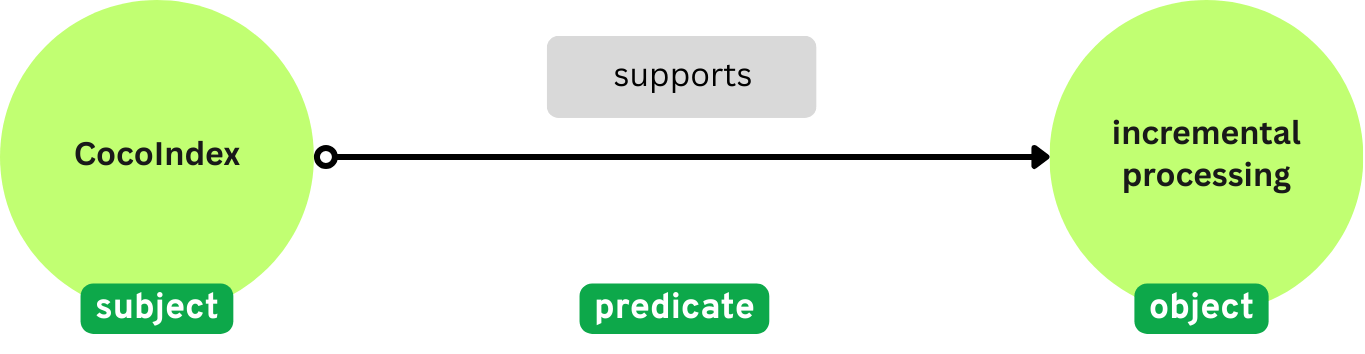
subject:表示该语句所针对的实体(例如,“CocoIndex”)。predicate:描述连接主体和对象的类型关系或属性(例如,“支持”)。object:表示主体通过谓词与之相关的实体或值(例如,“Incremental Processing”)。
这种结构表示诸如“CocoIndex 支持 Incremental Processing”之类的事实。其图形表示形式为:
 接下来,我们将使用
接下来,我们将使用 cocoindex.functions.ExtractByLlm 从文档中提取关系。
doc["relationships"]= doc["content"].transform( cocoindex.functions.ExtractByLlm( llm_spec=cocoindex.LlmSpec( api_type=cocoindex.LlmApiType.OPENAI, model="gpt-4o"), output_type=list[Relationship], instruction=("Please extract relationships from CocoIndex documents. ""Focus on concepts and ignore examples and code. ")))
doc["relationships"] 向每个文档添加一个新字段 relationships。output_type=list[Relationship] 指定转换的输出是一个 LTable。
收集关系
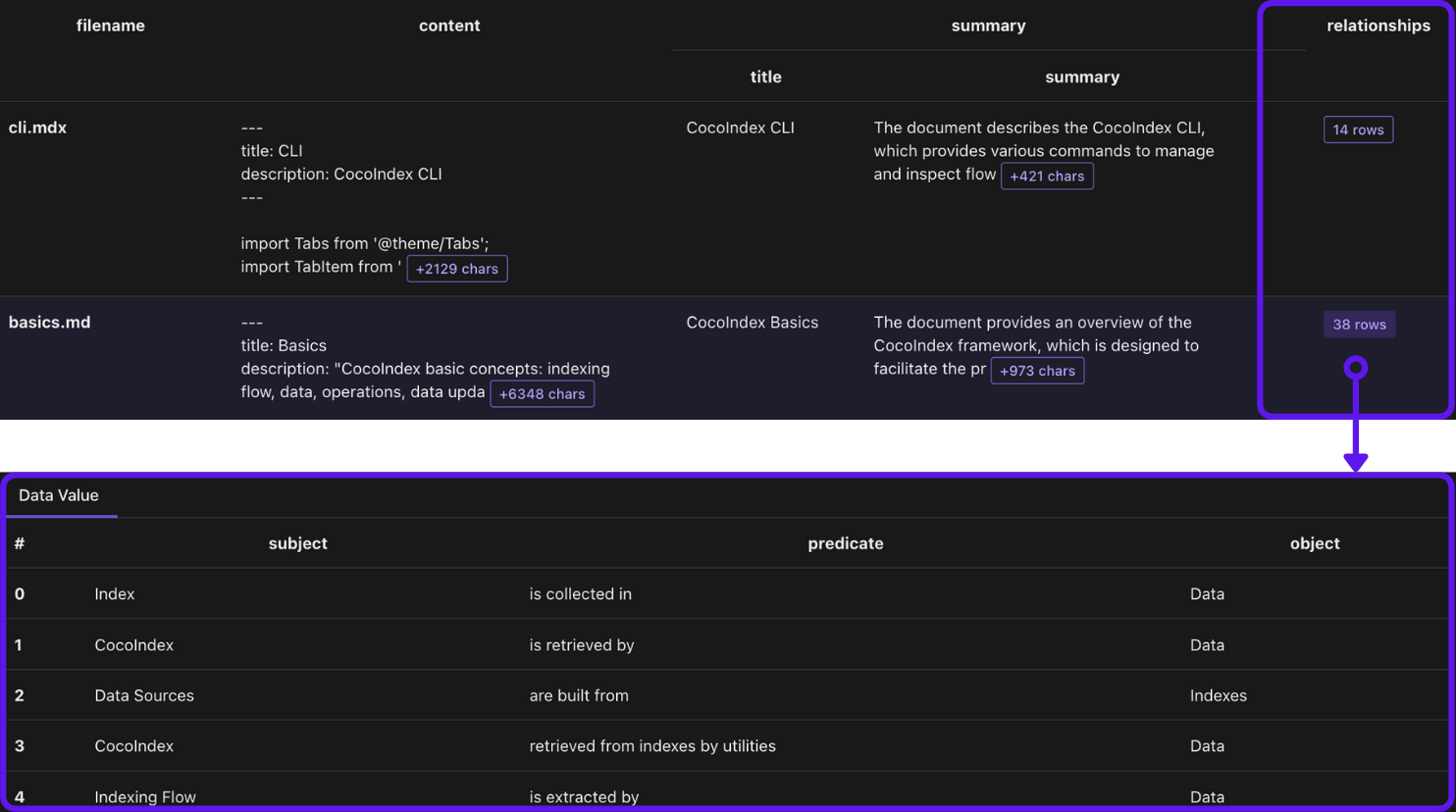
with doc["relationships"].row()as relationship:# relationship between two entities entity_relationship.collect(id=cocoindex.GeneratedField.UUID, subject=relationship["subject"],object=relationship["object"], predicate=relationship["predicate"],)# mention of an entity in a document, for subject entity_mention.collect(id=cocoindex.GeneratedField.UUID, entity=relationship["subject"], filename=doc["filename"],)# mention of an entity in a document, for object entity_mention.collect(id=cocoindex.GeneratedField.UUID, entity=relationship["object"], filename=doc["filename"],)
entity_relationship收集主体和对象之间的关系。entity_mention单独收集文档中实体的提及(作为主体或对象)。例如,core/basics.mdx有一个句子CocoIndex supports Incremental Processing。我们想收集:core/basics.mdx提到了CocoIndex。core/basics.mdx提到了Incremental Processing。
构建知识图谱
基本概念
Neo4j 的所有节点都需要两件事:
- 标签:节点的类型。例如,
Document、Entity。 - 主键字段:唯一标识节点的字段。例如,
Document节点的filename。
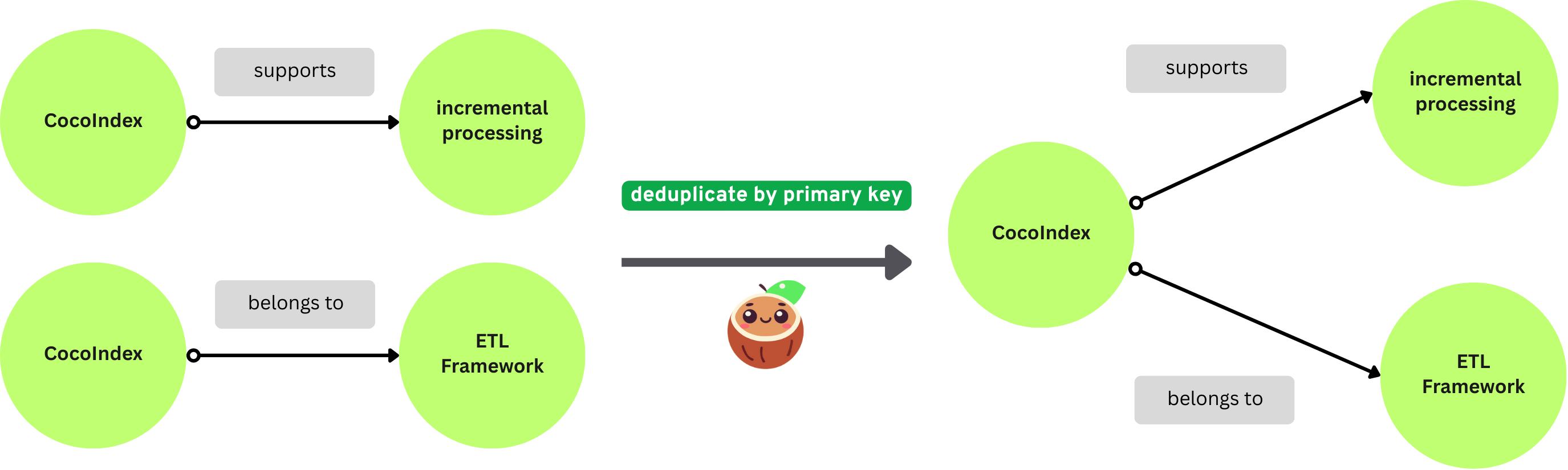
CocoIndex 使用主键字段来匹配节点并对其进行重复数据删除。如果您有多个具有相同主键的节点,CocoIndex 只保留其中一个。
 有两种方法可以映射节点:
有两种方法可以映射节点:
- 当您有一个仅用于节点的收集器时,您可以将其直接导出到 Neo4j。
- 当您有一个用于连接到节点的关系的收集器时,您可以从关系收集器中的选定字段映射节点。您必须声明节点标签和主键字段。
配置 Neo4j 连接:
conn_spec = cocoindex.add_auth_entry("Neo4jConnection", cocoindex.storages.Neo4jConnection( uri="bolt://localhost:7687", user="neo4j", password="cocoindex",))
将 Document 节点导出到 Neo4j
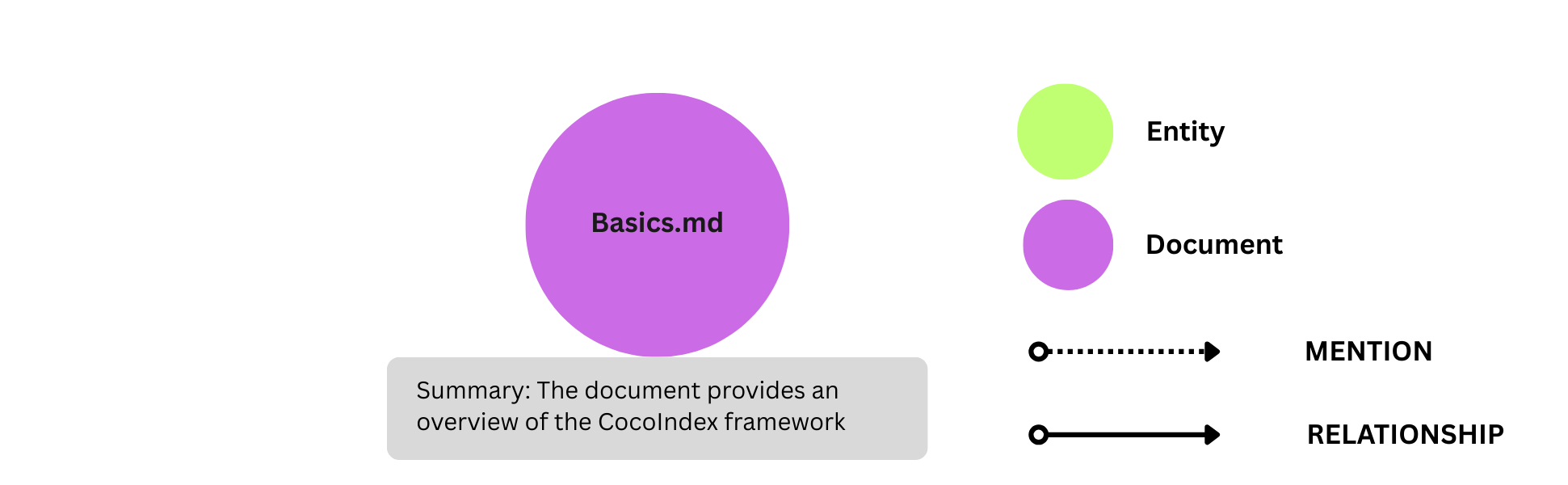
document_node.export("document_node", cocoindex.storages.Neo4j( connection=conn_spec, mapping=cocoindex.storages.Nodes(label="Document")), primary_key_fields=["filename"],)
这将从 document_node 收集器导出带有标签 Document 的 Neo4j 节点。
- 它声明 Neo4j 节点标签
Document。它指定filename作为主键字段。 - 它将
document_node收集器中的所有字段传输到带有标签Document的 Neo4j 节点。
将 RELATIONSHIP 和 Entity 节点导出到 Neo4j
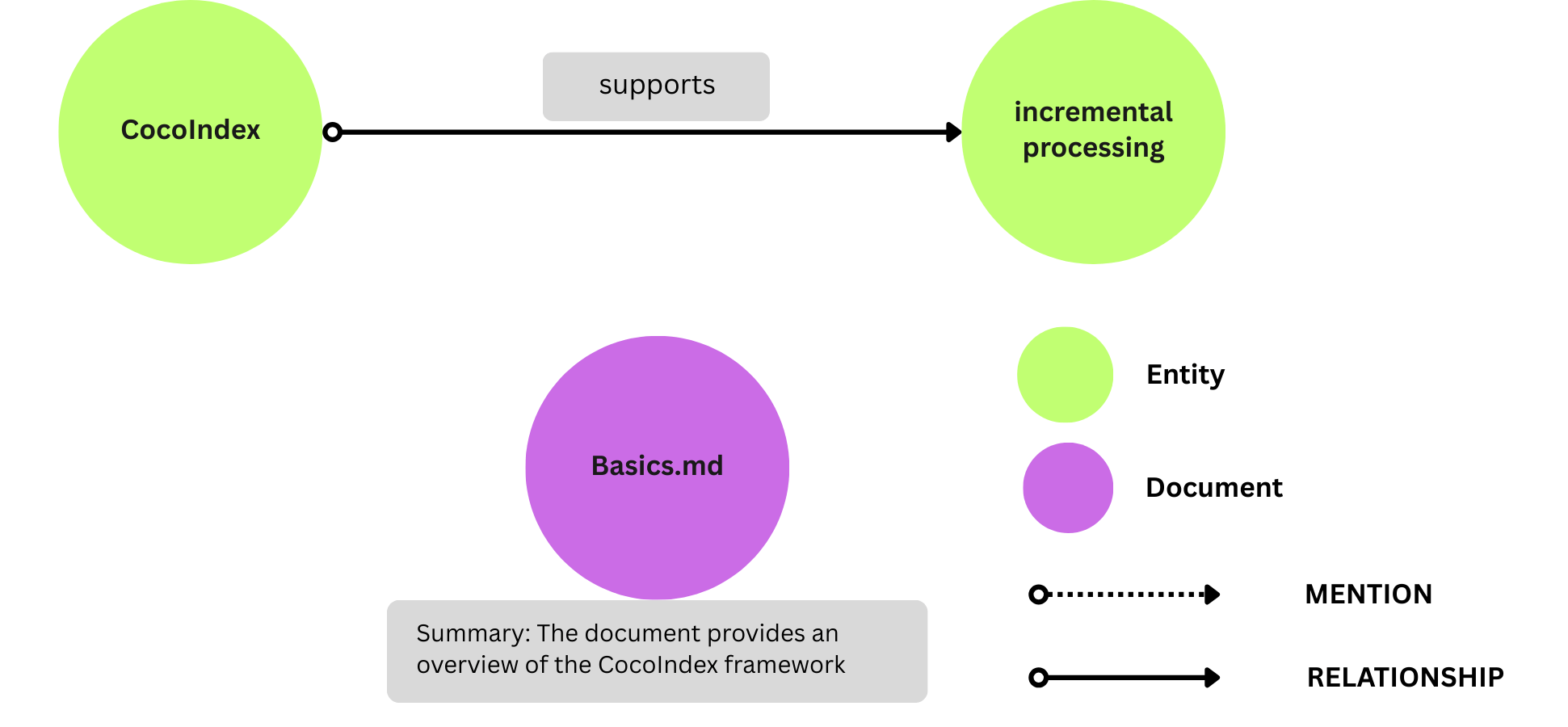
我们没有 Entity 节点的显式收集器。它们是 entity_relationship 收集器的一部分,并且字段在关系提取期间收集。
要将它们导出为 Neo4j 节点,我们需要首先声明 Entity 节点。
flow_builder.declare( cocoindex.storages.Neo4jDeclaration( connection=conn_spec, nodes_label="Entity", primary_key_fields=["value"],))
接下来,将 entity_relationship 导出到 Neo4j。
entity_relationship.export("entity_relationship", cocoindex.storages.Neo4j( connection=conn_spec, mapping=cocoindex.storages.Relationships( rel_type="RELATIONSHIP", source=cocoindex.storages.NodeFromFields( label="Entity", fields=[ cocoindex.storages.TargetFieldMapping( source="subject", target="value"),]), target=cocoindex.storages.NodeFromFields( label="Entity", fields=[ cocoindex.storages.TargetFieldMapping( source="object", target="value"),]),),), primary_key_fields=["id"],))
cocoindex.storages.Relationships 声明如何在 Neo4j 中映射关系。
在一个关系中,有:
- 一个源节点和一个目标节点。
- 连接源和目标的关系。请注意,不同的关系可能共享相同的源和目标节点。
NodeFromFields 从 entity_relationship 收集器中获取字段并创建 Entity 节点。
将 entity_mention 导出到 Neo4j。

entity_mention.export("entity_mention", cocoindex.storages.Neo4j( connection=conn_spec, mapping=cocoindex.storages.Relationships( rel_type="MENTION", source=cocoindex.storages.NodesFromFields( label="Document", fields=[cocoindex.storages.TargetFieldMapping("filename")],), target=cocoindex.storages.NodesFromFields( label="Entity", fields=[cocoindex.storages.TargetFieldMapping( source="entity", target="value")],),),), primary_key_fields=["id"],)
同样,我们在这里使用 cocoindex.storages.Relationships 将 entity_mention 导出到 Neo4j 关系。它通过以下方式创建关系:
- 从
entity_mention收集器创建Document节点和Entity节点。 - 使用关系
MENTION连接Document节点和Entity节点。
主函数
最后,流的主函数初始化 CocoIndex 流并运行它。
@cocoindex.main_fn()def_run():passif __name__ =="__main__": load_dotenv(override=True) _run()
查询和测试你的索引
🎉 现在一切都已设置完毕!
- 安装依赖项:
pip install -e .
- 运行以下命令来设置和更新索引。
python main.py cocoindex setuppython main.py cocoindex update
您将在终端中看到索引更新状态。例如,您将看到以下输出:
documents: 7 added, 0 removed, 0 updated
- (可选) 我使用 CocoInsight 来解决索引生成问题并了解管道的数据沿袭。它现在处于免费 Beta 版中,您可以尝试一下。运行以下命令来启动 CocoInsight:
python3 main.py cocoindex server -c https://cocoindex.io
然后打开 url https://cocoindex.io/cocoinsight。它只是连接到您的本地 CocoIndex 服务器,零管道数据保留。
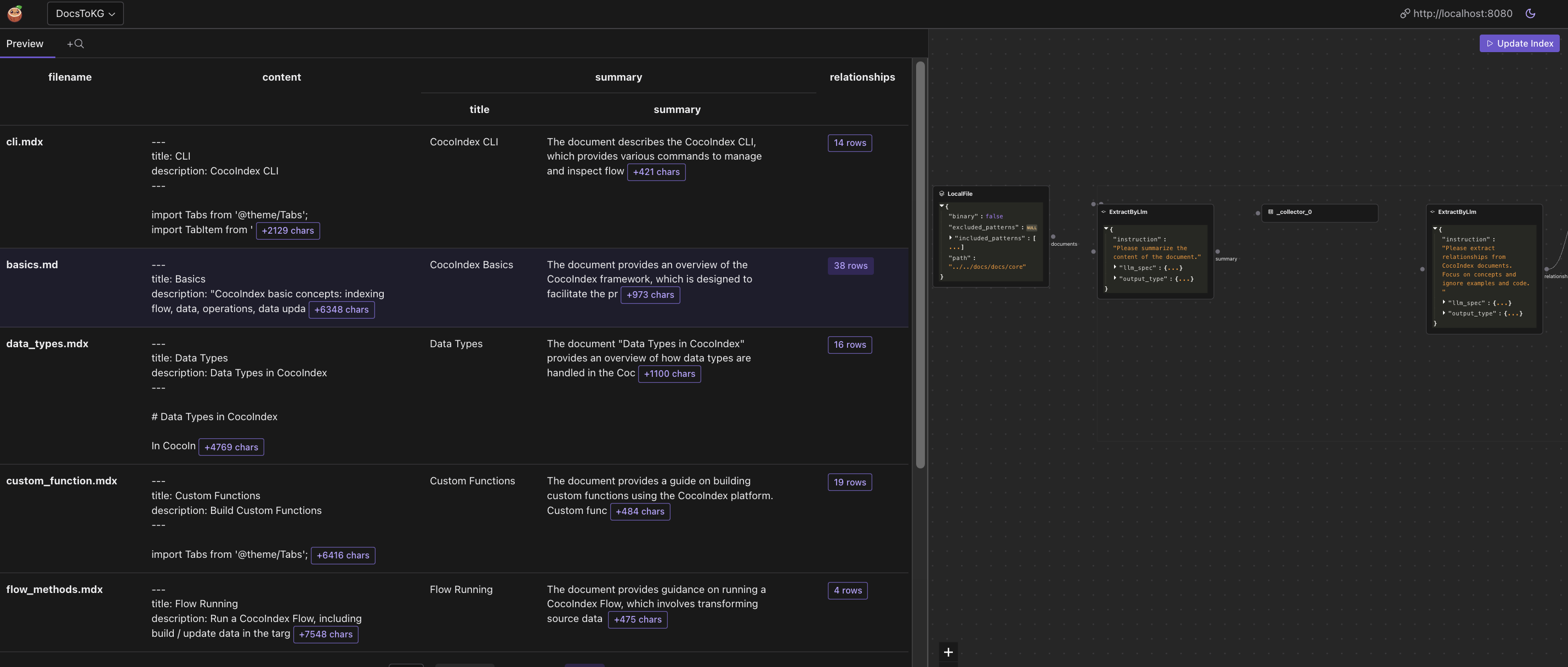
浏览知识图谱
构建知识图谱后,您可以在 Neo4j Browser 中浏览您构建的知识图谱。 对于开发环境,您可以使用以下凭据连接到 Neo4j browser:
- 用户名:
Neo4j - 密码:
cocoindex,该密码已在我们 docker compose config.yaml 中预先配置。
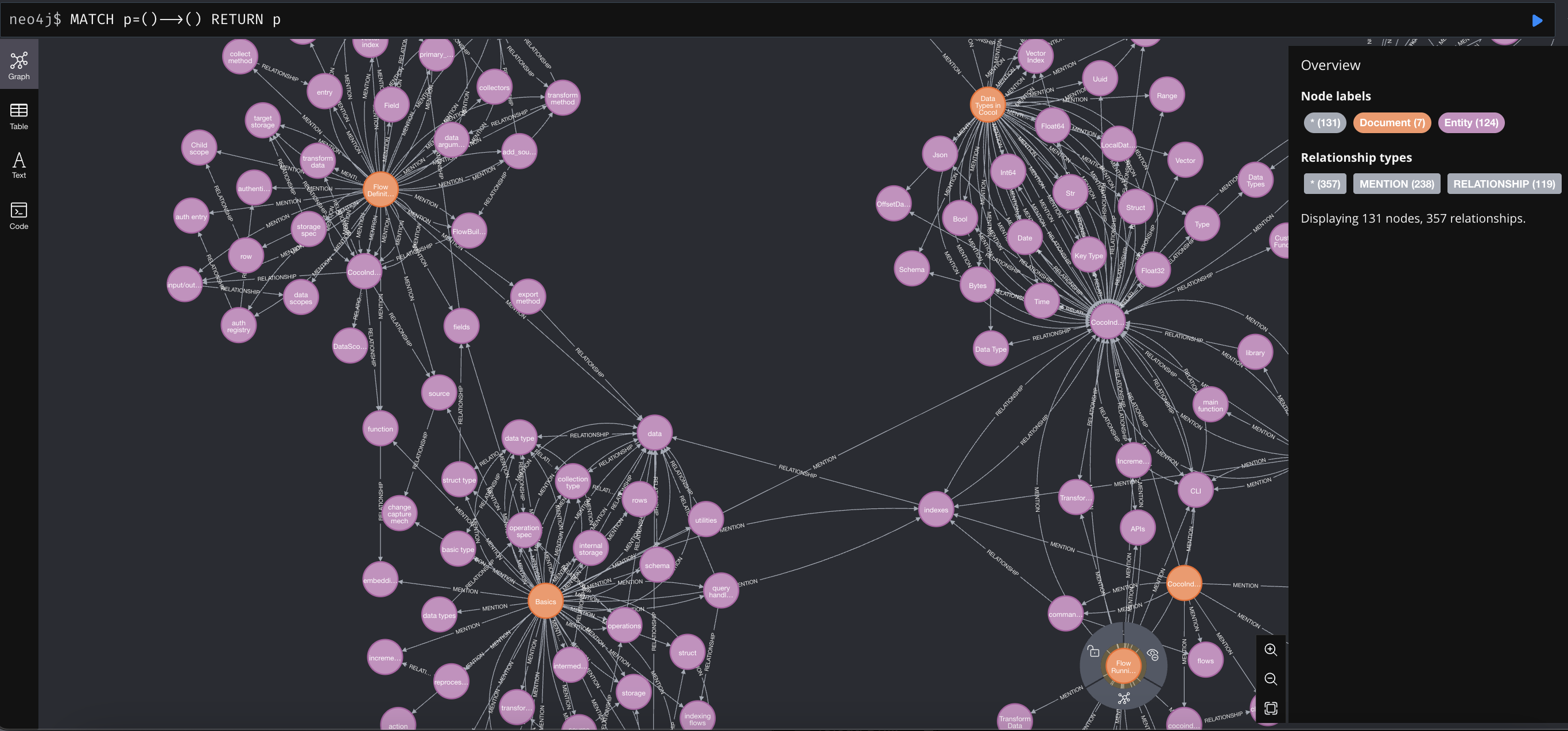
您可以在 http://localhost:7474 打开它,并运行以下 Cypher 查询以获取所有关系:
MATCH p=()-->() RETURN p
支持我们
我们正在不断改进,更多功能和示例即将推出。如果您喜欢这篇文章,请在 GitHub repo 上给我们一个星标 ⭐ 来帮助我们成长。 感谢阅读!
标签: